[ad_1]
- Prelims: Current events of international importance(Indo-Pacific, Regional forums, etc
- Mains GS Paper II: Multipolar World, Significance of Indo-Pacific for India, Indo-Pacific Region, Free and open Indo-Pacific, International organizations.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
- The S. President and his Chinese counterpart held a summit in San Francisco on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation conference.
- Aim: To resurrect a bilateral relationship
- The US and China established diplomatic ties in 1979.
Puucho ON THE ISSUE
Context
Phases in the US-China relationship:
- 19th century: American missionaries began to arrive in China and began to generate empathy for the nation.
- During World War II: US backed Chinese nationalists in their fight against Japanese occupation.
- The US tried to isolate China from 1949: when the communists prevailed over the nationalists.
- The 1970s: It saw the US and communist China come together to counter the Soviet Union.
- The 1980s: Beginning of an economic engagement that turned into a huge commercial and technological partnership from the 1990s.
- 21st century: some in the US began to see China as a potential threat.
- America believed that China’s growing economic prosperity would inevitably lead to greater democratization of its society.
- US-China rivalry has intensified in the past two years covering:
- trade
- technology
- naval activities in the South China Sea
How did relations sour between the U.S. and China?
What did the meet accomplish?
● The decision to restore military-to-military communications between the two nuclear weapons states
○ It is critical to prevent potentially catastrophic miscalculations.
○ The respective defense forces will now resume regular exchange of information under the Military Maritime Consultative Agreement that started in 1998.
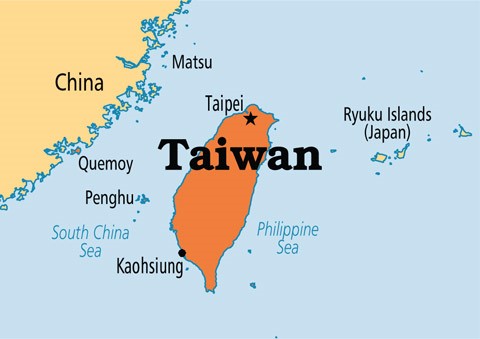
Taiwan Factor:
● Taiwan’s status remains a bone of contention between the US and China.
● China is pursuing the goal of its reunification into the mainland.
● Under the “one-China” policy, the US accepts China as the only legitimate government of China
● It does not endorse Taiwan as part of that country, and provides concrete security guarantees under the Taiwan Relations Act.
Recent Contention:
- China condemned Ms. Pelosi’s travel as constituting a serious violation of the status quo.
- China fired ballistic missiles off the Taiwan coast and conducted military drills as a deterrence exercise
- The US House Speaker received Taiwan’s President in California, the highest American official to do so on U.S. soil.
Where does the trade dispute stand?
Steps by USA:
- The US President issued an executive order in 2021: It blacklisted 59 defense and surveillance companies under the so-called “Chinese military-industrial complex”.
- The Trump administration in 2019 blacklisted several Chinese Artificial Intelligence (AI) start-ups for alleged human rights abuses in Xinjiang.
- The Biden administration enacted in 2022, further extended in 2023, on exports of advanced computer chips for the manufacture of semiconductors.
- The curbs bar U.S. and non-U.S. firms, whose products contain American technology, from supplying hardware and software to specific Chinese companies
- It prohibits American citizens and firms from collaborating with Chinese chip makers, except under special permission.
- Rationale: To undercut China’s strides in AI and supercomputing, which have powered its supersonic and nuclear weapons capability
- The US views it as detrimental to its security interests.
- Executive order Biden issued in August prohibiting U.S. investments in the high-tech arena.
Response by China:
- It clamped a ban on gallium and germanium exports, raw materials used in the production of microchips and weapons systems.
- These are listed in the U.S. inventory of materials critical for economic and national security.
- Curbs were imposed on exports of various types of graphite, a vital mineral for the production of electric vehicle batteries
- China has dominance in the global supply chain.
- The government further tightened its anti-espionage and data protection laws on the grounds of strengthening national security
- It forced firms to designate “for China” digital tools, set up China specific email ids and hive-off country exclusive servers.
Way Forward:
- The escalation of the bilateral dispute was epitomized in the muscular approach that the U.S. adopted to shore up global hegemony
- China’s quest for world military and technological supremacy that has crystallized under President Xi.
- There is in evidence a greater emphasis on exploring pragmatic avenues of coexistence through de-risking the two economies, rather than disengagement or ‘decoupling’.
- This is a significant shift, and the only hope in the short term that the superpowers will climb down from their hard positions.
- Stability in bilateral relations: The recent meeting between the two heads of states certainly imply that there is a move toward bringing in more stability into bilateral relations.
- The US’s three-pillar approach towards China — “invest, align, compete: This showcases the intent to deal with the threat posed by China without sliding into an inadvertent conflict.
QUESTION FOR PRACTICE
With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China.(UPSC 2014) (200 WORDS, 10 MARKS)
[ad_2]