[ad_1]
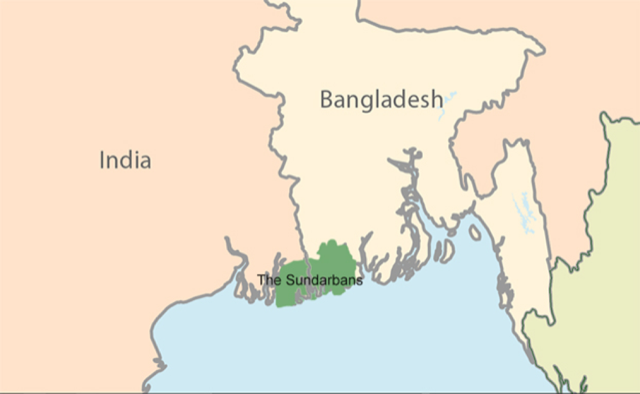
Sunderbans
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Biodiversity
In news The devastation caused by cyclone Yaas in West Bengal led to the huge ingress (entry) of saline water which affected thousands of acres of agricultural land.
- The West Bengal government has been distributing relief and compensation and also salt tolerant varieties of paddy to farmers.
What are the consequences of the ingress of saline water?
- It kills standing crops and increases salinity of the soil
- It makes the cultivation of regular high-yielding varieties almost impossible for the next few years which may result in food crisis in the region
About Sundarbans
- Sundarbans is a vast contiguous mangrove forest ecosystem in the coastal region of Bay of Bengal spread over India and Bangladesh on the delta (world’s largest) of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers.
- It contains the world’s largest mangrove forests.
- It is the only mangrove forest in the world inhabited by tigers.
- Sundarbans Tiger Reserve was created in 1973.
- Sundarbans National Park, established in 1984, constitutes a core region within the tiger reserve.
- It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1987.
- Sunderbans was designated as a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2001.
- Sundarban Wetland, India was recognised as the ‘Wetland of International Importance’ under the Ramsar Convention in January 2019.
News Source: TH
[ad_2]