[ad_1]
GS Paper 3
Syllabus: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context:
Cooperation Minister has highlighted that cooperative banks will not be given a “second-grade” treatment but they should adopt modern and transparent banking methods to stay in the competition.
Status: As per RBI, as of March 2019, there were 1,544 urban co-operative banks, and 96,248 rural co-operative banks in the country.
Need for modernization:
- Negligible participation: There were more than 195 cooperative banks that were more than 100 years old. Despite this, the role of urban cooperative banks is negligible in the total banking sector in terms of deposit and advance payment.
- UCBs account for only 3.25 per cent of the total bank deposits and 2.69 per cent of the total advances in the country.
- Symmetric development of Urban cooperative: There are 1,534 urban cooperative banks, and 54 scheduled urban cooperative banks but the development is uneven. The symmetric development of cooperative banks will help sustain competition in future.
- Need to look after small and marginal sections: Urban State Cooperative Banks need to be strengthened for the upliftment of that section, and to make them participants in the process of development and a stakeholder in the country’s economy.
What should be done:
- Adopt modern and transparent banking methods to stay in competition e.g. computerization of accounting process
- Engage younger people in management roles
- Engage professionals to run day-to-day affairs
- Treating UCB equally in government policies in respect of taxation, BR Act [The Banking Regulation Act, 1949] or the Reserve Bank’s norms.
- Responsibility lies with the cooperative sector: It is the cooperatives’ responsibility to establish trustworthiness and earn people’s faith as well as win the confidence of the RBI and the government.
- Undertake institutional reforms like transparency in recruitment and implementation of a robust accounting system, which is necessary for their growth.
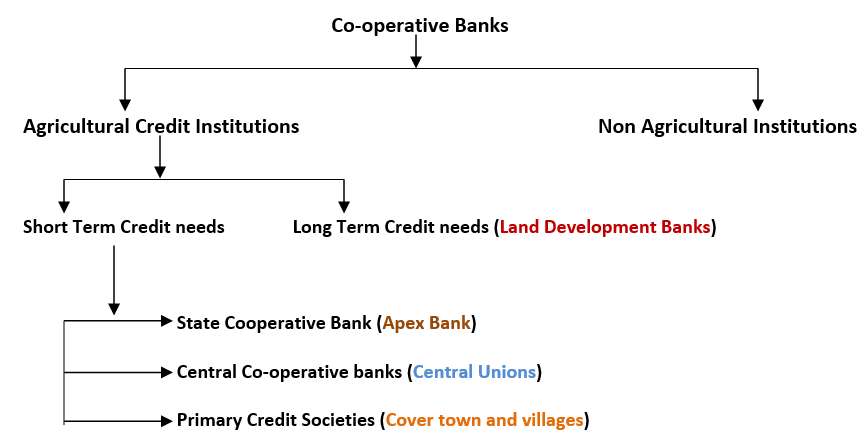
Cooperative Bank
Cooperative Banking
A Co-operative bank is a financial entity which belongs to its members, who are at the same time the owners and the customers of their bank.
Governance: They are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act of the State concerned or the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 and goverened under the Banking Regulations Act, 1949 and Banking Laws (Cooperative Societies) Act, 1955.
Features of Cooperative Banks:
- They are Customer Owned: Co-operative bank members are both customer and owner of the bank.
- Democratic in nature: Co-operative members also own it and they democratically elect a board of directors. Members usually have equal voting rights, (as per the principle of “one person, one vote”)
- Profit distribution: Part of the profit, benefits or surplus is usually allocated to constitute reserves and a part of this profit can also be distributed to the co-operative members.
- They play important role in Financial Inclusion of unbanked rural masses.
RBI appointed committee categorised UCB into four tiers for regulatory purposes:
- Tier 1 (having deposits up to Rs 100 crore)
- Tier 2 (deposits between Rs 100 crore and Rs 1,000 crore)
- Tier 3 (deposits between Rs 1,000 crore and Rs 10,000 crore)
- Tier 4 (deposits more than Rs 10,000 crore)
For UCBs the minimum Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) for them could vary from 9% to 15% and Tier-4 UCBs has to follow the Basel III prescribed norms.
Insta Links
Practice Questions:
Q. Co-operative banks in India form the backbone for the delivery of credit to rural areas. However, for cooperative banks to be regulated and supervised better, RBI needs to ramp up its supervisory capacity. Elucidate. (15M)
Q. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
Answer: b
Q. Consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks are Regional Rural Banks
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: b
Sources: The Hindu, Indian Express
[ad_2]