[ad_1]
GS Paper 3:
Topics Covered: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context:
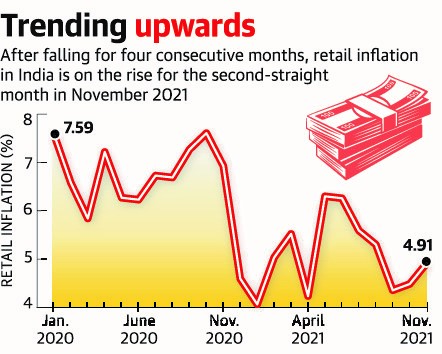
India’s retail inflation hardened for the second month in a row in November, touching 4.91% from 4.48% recorded in October, with urban parts experiencing a sharper rise in prices at a pace of 5.54% and vegetable prices jumping 7.45% from the previous month.
Concern:
This suggests that upward price pressures persist, owing to the rise in input and commodity costs, as reflected in the wholesale price inflation touching a five-month high of 12.54% in October. This will affect inflation targeting by the RBI.
What is inflation targeting?
- It is a central banking policy that revolves around adjusting monetary policy to achieve a specified annual rate of inflation.
- The principle of inflation targeting is based on the belief that long-term economic growth is best achieved by maintaining price stability, and price stability is achieved by controlling inflation.
Inflation Targeting Framework:
Now there is a flexible inflation targeting framework in India (after the 2016 amendment to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934).
Who sets the inflation target in India?
The amended RBI Act provides for the inflation target to be set by the Government of India, in consultation with the Reserve Bank, once every five years.
Current Inflation Target:
The Central Government has notified 4 per cent Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation as the target for the period from August 5, 2016, to March 31, 2021, with the upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent and the lower tolerance limit of 2 per cent.
InstaLinks:
Prelims Link:
- What is the current inflation target?
- Who sets it?
- What is the monetary policy committee (MPC)?
- Functions.
- Composition.
Sources: the Hindu.
[ad_2]