[ad_1]
GS Paper 3:
Topics Covered: Awareness in space.
Polar-Areas Stellar-Imaging in Polarisation High-Accuracy Experiment (PASIPHAE) is an international collaborative sky surveying project.
- Scientists aim to study the polarisation in the light coming from millions of stars.
Background:
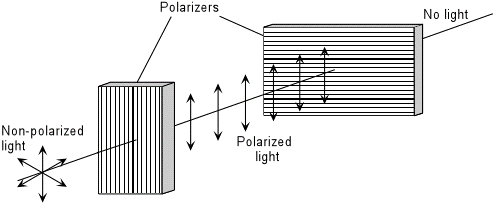
Polarization is a property of light that represents the direction that the light wave oscillates.

How will the survey be carried out?
- The survey will use two high-tech optical polarimeters to observe the northern and southern skies, simultaneously.
- It will focus on capturing starlight polarisation of very faint stars that are so far away that polarisation signals from there have not been systematically studied.
- The distances to these stars will be obtained from measurements of the GAIA satellite.
- By combining these data, astronomers will perform a maiden magnetic field tomography mapping of the interstellar medium of very large areas of the sky using a novel polarimeter instrument known as WALOP (Wide Area Linear Optical Polarimeter).
Significance of the project:
The theory is that a small fraction of CMB radiation emitted during the universe’s rapid inflationary phase should have its fingerprints on a specific kind of polarisation, known technically as B-mode signals. These B-modes are theorised to have arisen as a result of powerful gravitational waves seen during inflation.
However, these signals have been difficult to isolate because of the enormous amounts of polarised radiation in our own Milky Way, caused by large dust clouds that fill the galaxy.
- In essence, PASIPHAE endeavours to ascertain the effect of these obstacles, so we can, ultimately, learn how things played out in the early universe.
Insta Curious:
Know different properties of light Click here,
InstaLinks:
Prelims Link:
- What is polarization?
- About PASIPHAE.
- About GAIA Satellite.
Sources: Indian Express.
[ad_2]