[ad_1]
Editorials Quiz 2021-22
Information
Introducing yet another ingenious course, InsightsIAS is excited to announce our new initiative QUED – Questions from Editorials. Considering the number of questions that appeared from Editorials in previous year UPSC Prelims Examinations, we feel it is wise for students to cover Editorials from Prelims point of view as well in order to achieve that extra edge. Although, we have covered important editorials separately in our Editorial Section as well as under Secure Initiative, MCQ practice can prove to be crucial for better performance and guaranteed result.
We strongly recommend you at add QUED along with Static Quiz ,Current Affairs Quiz and RTM for your Daily MCQ practice.
We will be posting 5 MCQs at 11am everyday from Monday to Saturday on http://www.insightsonindia.com. QUED will be available under QUIZ menu.
We hope students utilize this initiative to the best of advantage. 🙂
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
-
Question 1 of 5
Consider the following statements regarding Monetary Policy.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is vested with the responsibility of conducting monetary policy under the provisions of Agreement on Monetary Policy Framework Act.
- The primary objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability and achieve growth.
- The inflation target is set by the Reserve Bank of India in consultation with Government of India, once in every five years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
CorrectSolution: b)
- Monetary policy refers to the policy of the central bank with regard to the use of monetary instruments under its control to achieve the goals specified in the Act.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is vested with the responsibility of conducting monetary policy. This responsibility is explicitly mandated under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- The primary objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth. Price stability is a necessary precondition to sustainable growth.
- In May 2016, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934 was amended to provide a statutory basis for the implementation of the flexible inflation targeting framework.
- The amended RBI Act also provides for the inflation target to be set by the Government of India, in consultation with the Reserve Bank, once in every five years. Accordingly, the Central Government has notified in the Official Gazette 4 per cent Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation as the target for the period from August 5, 2016 to March 31, 2021 with the upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent and the lower tolerance limit of 2 per cent.
- Prior to the amendment in the RBI Act in May 2016, the flexible inflation targeting framework was governed by an Agreement on Monetary Policy Framework between the Government and the Reserve Bank of India of February 20, 2015.
IncorrectSolution: b)
- Monetary policy refers to the policy of the central bank with regard to the use of monetary instruments under its control to achieve the goals specified in the Act.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is vested with the responsibility of conducting monetary policy. This responsibility is explicitly mandated under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- The primary objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth. Price stability is a necessary precondition to sustainable growth.
- In May 2016, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934 was amended to provide a statutory basis for the implementation of the flexible inflation targeting framework.
- The amended RBI Act also provides for the inflation target to be set by the Government of India, in consultation with the Reserve Bank, once in every five years. Accordingly, the Central Government has notified in the Official Gazette 4 per cent Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation as the target for the period from August 5, 2016 to March 31, 2021 with the upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent and the lower tolerance limit of 2 per cent.
- Prior to the amendment in the RBI Act in May 2016, the flexible inflation targeting framework was governed by an Agreement on Monetary Policy Framework between the Government and the Reserve Bank of India of February 20, 2015.
-
Question 2 of 5
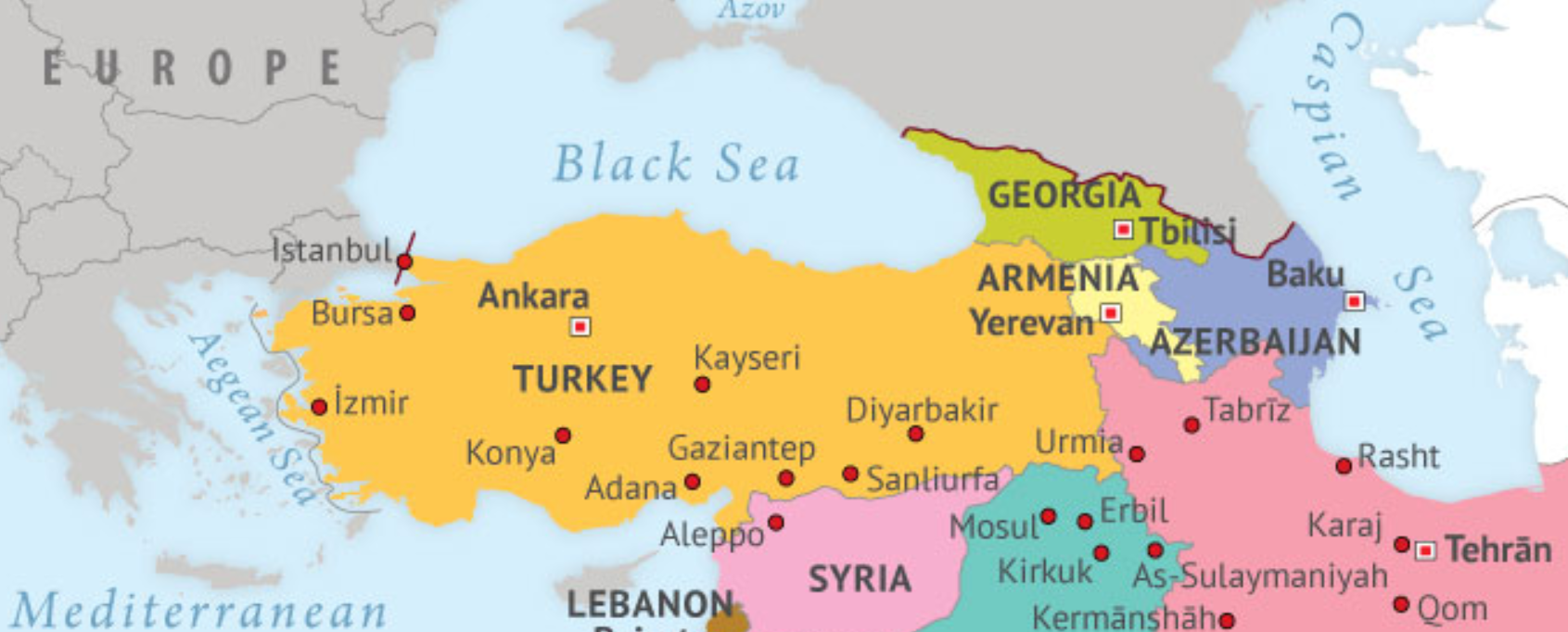
The country with the longest coastline on the Black Sea is
CorrectSolution: a)
 Incorrect
IncorrectSolution: a)

-
Question 3 of 5
India’s economy is showing decisive signs of a ‘V-shaped’ recovery in 2021. What does ‘V-shaped’ recovery mean?
CorrectSolution: b)
In V-shaped recovery the economy quickly recoups lost ground and gets back to the normal growth trend-line.

The Z-shaped recovery is the most-optimistic scenario in which the economy quickly rises like a phoenix after a crash. It more than makes up for lost ground (think revenge-buying after the lockdowns are lifted) before settling back to the normal trend-line, thus forming a Z-shaped chart.
A U-shaped recovery is a scenario in which the economy, after falling, struggles and muddles around a low growth rate for some time, before rising gradually to usual levels.
A W-shaped recovery is a dangerous creature — growth falls and rises, but falls again before recovering yet again, thus forming a W-like chart.
The L-shaped recovery is the worst-case scenario, in which growth after falling, stagnates at low levels and does not recover for a long, long time.
IncorrectSolution: b)
In V-shaped recovery the economy quickly recoups lost ground and gets back to the normal growth trend-line.

The Z-shaped recovery is the most-optimistic scenario in which the economy quickly rises like a phoenix after a crash. It more than makes up for lost ground (think revenge-buying after the lockdowns are lifted) before settling back to the normal trend-line, thus forming a Z-shaped chart.
A U-shaped recovery is a scenario in which the economy, after falling, struggles and muddles around a low growth rate for some time, before rising gradually to usual levels.
A W-shaped recovery is a dangerous creature — growth falls and rises, but falls again before recovering yet again, thus forming a W-like chart.
The L-shaped recovery is the worst-case scenario, in which growth after falling, stagnates at low levels and does not recover for a long, long time.
-
Question 4 of 5
Consider the following statements regarding South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
- Its secretariat is based in India.
- The SAARC maintains permanent diplomatic relations at the United Nations as an observer.
- Decisions at all levels are to be taken on the basis of unanimity and bilateral and contentious issues are excluded from the deliberations of the Association.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
CorrectSolution: d)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia.
The SAARC was founded in Dhaka on 8 December 1985. Its secretariat is based in Kathmandu, Nepal. The organization promotes development of economic and regional integration. It launched the South Asian Free Trade Area in 2006. The SAARC maintains permanent diplomatic relations at the United Nations as an observer and has developed links with multilateral entities, including the European Union.
Decisions at all levels are to be taken on the basis of unanimity and bilateral and contentious issues are excluded from the deliberations of the Association.
IncorrectSolution: d)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia.
The SAARC was founded in Dhaka on 8 December 1985. Its secretariat is based in Kathmandu, Nepal. The organization promotes development of economic and regional integration. It launched the South Asian Free Trade Area in 2006. The SAARC maintains permanent diplomatic relations at the United Nations as an observer and has developed links with multilateral entities, including the European Union.
Decisions at all levels are to be taken on the basis of unanimity and bilateral and contentious issues are excluded from the deliberations of the Association.
-
Question 5 of 5
Consider the following statements regarding the instruments of Monetary Policy.
- Repo rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) consists of only overnight auctions.
- The Reserve Bank also conducts variable interest rate reverse repo auctions, as necessitated under the market conditions.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
CorrectSolution: b)
- Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- Reverse Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank absorbs liquidity, on an overnight basis, from banks against the collateral of eligible government securities under the LAF.
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF): The LAF consists of overnight as well as term repo auctions. Progressively, the Reserve Bank has increased the proportion of liquidity injected under fine-tuning variable rate repo auctions of range of tenors. The aim of term repo is to help develop the inter-bank term money market, which in turn can set market based benchmarks for pricing of loans and deposits, and hence improve transmission of monetary policy. The Reserve Bank also conducts variable interest rate reverse repo auctions, as necessitated under the market conditions.
IncorrectSolution: b)
- Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- Reverse Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank absorbs liquidity, on an overnight basis, from banks against the collateral of eligible government securities under the LAF.
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF): The LAF consists of overnight as well as term repo auctions. Progressively, the Reserve Bank has increased the proportion of liquidity injected under fine-tuning variable rate repo auctions of range of tenors. The aim of term repo is to help develop the inter-bank term money market, which in turn can set market based benchmarks for pricing of loans and deposits, and hence improve transmission of monetary policy. The Reserve Bank also conducts variable interest rate reverse repo auctions, as necessitated under the market conditions.
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE for Motivation and Fast Updates
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Motivational and New analysis videos
[ad_2]