[ad_1]
GS Paper 3
Syllabus: Agriculture Credit
Source: PIB
Context: The Ministry of Cooperation has introduced Model Bye-Laws to revitalize Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS).
What are Model Bye-Laws?
The Model Bye-Laws empower PACS to diversify by engaging in over 25 business activities, including dairy, fishery, godowns, credit services, and more. Provisions ensure inclusive membership with adequate representation for women and Scheduled Castes/Scheduled Tribes. These guidelines aim to govern the grassroots functioning of PACS, outlining their structure and operations. The purpose is to enhance economic viability and expand their role in rural areas.
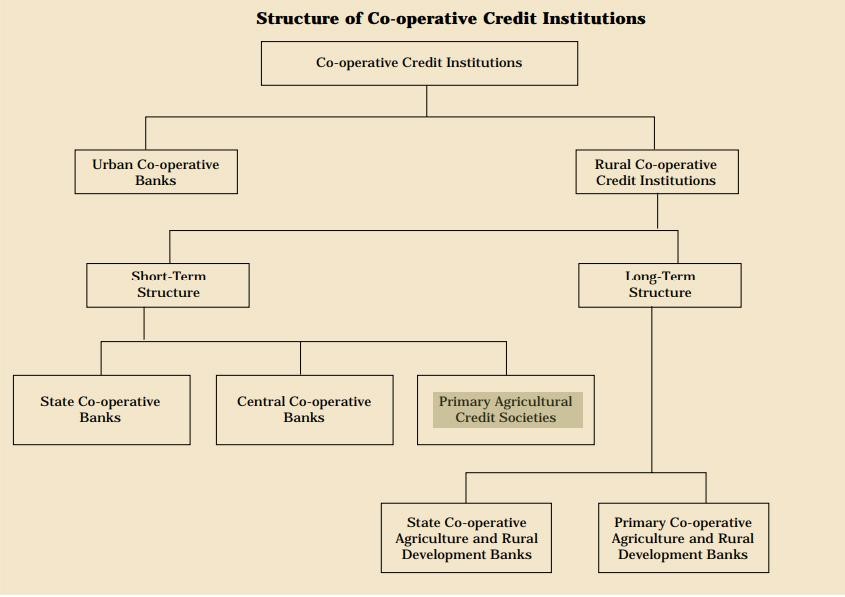
Status of PACS in India:
- With approximately 13 crore farmers as members, PACS are integral to the country’s three-tier Short-term cooperative credit system.
About PACS:
- Established in 1904, PACS contribute significantly to financial inclusion with minimal paperwork, facilitating timely access to capital for farmers.
Role of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) for Rural and Agricultural Development in India:
| Role | Description |
| Financial Inclusion | It is a village-level institution that works directly with rural residents. It encourages agriculturists to save, accepts deposits from them, makes loans to deserving borrowers, and collects repayments. |
| Extending Credit | PACS have the capacity to extend credit with minimal paperwork within a short time. |
| Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Scheme | The KCC scheme, launched by the government, is facilitated through PACS. It provides farmers with a simplified credit card to access short-term credit for crop cultivation and allied activities. (e.g., they account for 41% of all KCC loans.) |
| Providing Agricultural Inputs | It supplies agricultural inputs like fertilizers, seeds, insecticides, and implements to farmers. |
| Supporting Small and Marginal Farmers | Among these KCC loans provided by PACS, a remarkable 95% (approximately 3 crore farmers) are availed by Small and Marginal farmers through PACS. |
| Marketing of Agricultural Produce | PACS assist farmers in the marketing of their agricultural produce and provides support in finding better markets, thereby improving farmers’ income and reducing dependency on middlemen. (e.g., in Kerala, PACS play an active role in marketing cash crops like rubber and spices.) |
| Training and Capacity Building | PACS conduct various training programs and workshops to enhance the financial literacy and awareness of farmers, empowering them to make informed financial decisions. (e.g., in Maharashtra, training programs on modern agricultural practices, organic farming, etc.) |
Issues with PACS:
- Inadequate Coverage: Coverage is low in some areas, especially in the north-east. Only 50% of rural households are covered as members.
- Inadequate Resources: PACS resources are insufficient for the short- and medium-term credit needs of the rural economy.
- Overdue and NPAs: RBI reports lending of Rs 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs 72,550 crore.
- Overdue hamper the circulation of loanable funds, diminish borrowing and lending power and tarnish the image of societies.
Initiatives taken to strengthen the functioning and effectiveness of PACS in India:
- Computerisation: The budget 2023 has announced Rs 2,516 crore for Computerisation of 63,000 Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) over the next five years, with the aim of bringing greater transparency and accountability in their operations and enabling them to diversify their business and undertaking more activities.
- Credit Linkage with NABARD: PACS are linked to the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), enabling them to access financial resources and expertise for better functioning.
- Making PACS multidimensional: The model bylaws, prepared by the Ministry of Cooperation after consultation with all stakeholders, will enable PACS to diversify its business by undertaking more than 25 different economic activities, including, dairy, fisheries, godowns, custom hiring centres, fair price shops, LPG/diesel/petrol distributorship, etc.
- Multistate Cooperative Societies have been formed for seeds, marketing of organic farming and export of farmers’ produce.
- Common Service Centres (CSCs): Delivery of CSC services through PACS is a big step towards strengthening them, which will allow PACS to provide facilities like Common Service Centres in the country and its benefits will reach crores of people living in rural areas in the country.
Conclusion
PACS form the bedrock of India’s cooperative movement, and continuous efforts are essential to enhance their viability and contribute to sustainable rural and agricultural development.
Mains Links
Q.“In the villages itself no form of credit organization will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural fi nance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural fi nance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (UPSC 2014)
Q1. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: B
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2021)
They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B
[/su_table]
[ad_2]