[ad_1]
- Prelims: Science and technology, Artificial intelligence(AI), Generative AI, Big Data, GANs, ChatGPT1 tool, DALL.E2 etc
- Mains GS Paper III and IV: Significance of technology for India, AI, indigenisation of technology and development of new technology.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
- The Generative AI revolution will potentially unleash a wave of technical and social change.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) alone are predicted to add $6(two point six)trillion-$4.4(four point four)trillion annually to the global economy.
- The ongoing pilot of Jugalbandi Chatbot in rural India (powered by ChatGPT)
Puucho ON THE ISSUE
Context
Artificial intelligence(AI):
- It is a branch of computer science dealing with the simulation of intelligent behavior in computers.
- It describes the action of machines accomplishing tasks that have historically required human intelligence.
- It includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self algorithms etc.
- g: Facebook’s facial recognition software which identifies faces in the photos we post, the voice recognition software that translates commands we give to Alexa, etc are some of the examples of AI already around us.
Generative AI:
- It is a cutting-edge technological advancement that utilizes machine learning and artificial intelligence to create new forms of media, such as text, audio, video, and animation.
- With the advent of advanced machine learning capabilities: It is possible to generate new and creative short and long-form content, synthetic media, and even deep fakes with simple text, also known as prompts.
AI innovations:
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
- LLMs (Large Language Models)
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformers)
- Image Generation to experiment
- Create commercial offerings like DALL-E for image generation
- ChatGPT for text generation.
- It can write blogs, computer code, and marketing copies and even generate results for search queries.
Uses of Generative AI:
- Generative AI can craft sales, marketing, and brand messaging.
- Agencies can generate personalized social media posts, blogs, and marketing text and video copies by providing a text prompt to a Generative AI service, like ChatGPT.
- Service can quickly iterate different text by simply tweaking the prompt to effectively communicate with the audience.
- E(a generative image generation service): It can also generate original imagery to align with the branding.
- GitHub, Copilot6 and ChatGPT1 can generate code and help with developer productivity.
- It can suggest entire functions, snippets, and even fully functioning modules and generate code in real-time right in your editor.
- ChatGPT can also help you write code to build a technology service or integration quickly.
- Generating synthetic data for data augmentation and creating additional training data to train and test AI models to experiment at scale.
- It can sift through numerous legal research materials and produce a pertinent, specific, and actionable summary.
- It can reduce the countless hours of human research and enable them to focus on more complex and exciting problems.
- ChatGPT: It can assist in providing answers to complex queries and augment search algorithms to generate responses to complex search queries.
- It can accelerate the discovery of new research, drafting and synthesizing documents and reports.
- It can also help create and simulate complex engineering, design, and architecture.
- It can help speed up the iterative development and testing of novel designs.
- Architecture, machine design, and even house floor plans are all made by Generative Image and video technology.
- It can let engineers and consumers design and iterate over floor plans and architectures with as little as a text prompt or vocal command.
- It can also help health professionals with their medical diagnosis.
- AI can generate potential and alternative treatments personalized to patients’ symptoms and medical history.
- For instance, DeepMind AlphaFold can predict the shape of protein.
What is the news?
- The ongoing pilot of Jugalbandi Chatbot in rural India (powered by ChatGPT)
- It will serve as a universal translator
- accepting queries in local languages
- retrieving answers from English-language sources
- presenting them back to users in their native language.
- It can democratize access to information and improve the economic well-being of millions of people.
Concerns:
- AI powered tools are enabling bad actors to create artificial entities that are indistinguishable from humans online (via speech, text, and video).
- Bad actors can misrepresent themselves or others
- They potentially can launch a barrage of variations on old harms such as misinformation and disinformation, security hacks, fraud, hate speech, shaming, etc.
- Example: In the U.S., an AI generated image of the Pentagon burning spooked equity markets.
- Fake Twitter and Instagram users promulgating strong political views have been reposted millions of times, contributing to polarized politics online.
- Cloned AI voices have been used to circumvent bank customer authentication measures.
- Examples:
- An individual in Belgium was allegedly driven to suicide with his conversations with an LLM.
- Recent elections in Turkey were marred by AI generated deep fakes.
- Role of bad actors in elections: Over one billion voters will head to polls across the U.S., India, the EU, the U.K., and Indonesia in the next two years,
- The risk of bad actors harnessing Generative AI for misinformation and election influence is steadily growing.
- Examples:
What steps need to be taken?
- Regulatory proposal: All digital assistants (aka ‘bots’) to self-identify as such, and to criminalize fake media.
- Established companies may ensure their AI bots self-identify, and only publish valid information.
- However, bad actors will simply disregard the rule
- capitalizing on the trust created by compliant companies.
- There is a need for a more conservative assurance paradigm, whereby all digital entities are assumed to be AI bots or fraudulent businesses unless proven otherwise.
- Regulation is necessary but not sufficient: A broader approach should be considered to improve Internet safety and integrity.
- Recent research at the Harvard Kennedy School(Identity assurance framework): Identity assurance ensures trust between interacting parties
- It verifies the authenticity of the involved entities, enabling them to have confidence in each other’s claimed identities.
- key principles:
- It can be open to the numerous credential types emerging around the world
- It is not specific to any single technology or standard, and yet provides privacy protections.
- This identity assurance framework would be extended to humans, bots, and businesses.
- More than 50 countries have initiatives underway to develop or issue digital identity credentials: It will form the foundation of this identity assurance framework.
- India, with Aadhaar, is in a leadership position to establish online identity assurance safeguards.
- European Union: It is establishing a new identity standard which will also support online identity assurance, but full user adoption will likely take the rest of this decade.
- However, bad actors will simply disregard the rule
Information integrity:
- Information integrity ensures that the content being accessed is authentic and was published by the person it claims to be published by.
- Identity assurance is also tied to the question of information integrity.
- This credibility comes from three pillars:
- Source validation, which is to enable verifiability that information comes from a known source/publisher/individual.
- Content integrity: Which is to enable verifiability that the information has not been tampered with.
- Information validity: This is contentious but can be realized with automated fact-checking and crowdsourced reviews.
- Identity assurance touches privacy versus surveillance, civil liberty versus security, anonymity versus accountability.
- Information integrity raises the questions of censorship and the timeless question of ‘who defines the truth.
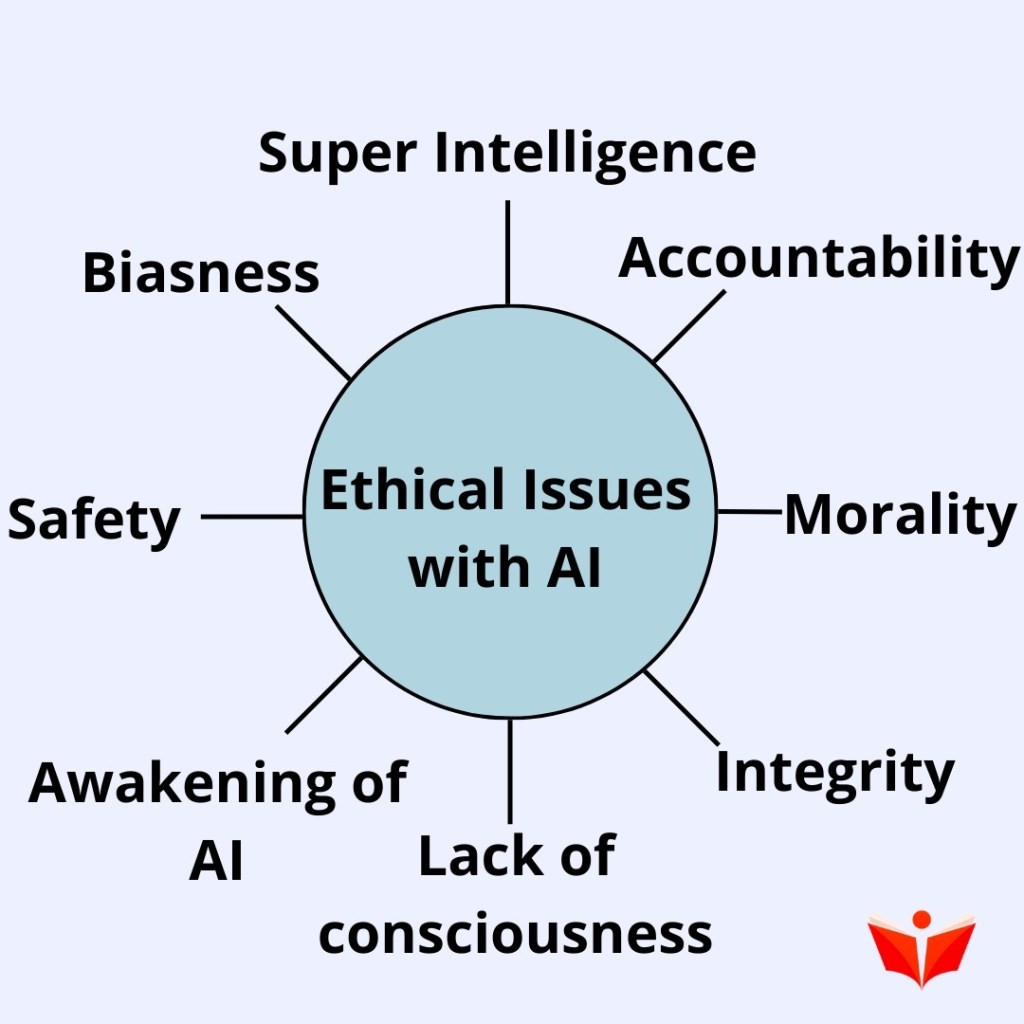
Ethical Issues with AI:
Way Forward
- As we consider rebalancing between Information integrity and identity assurance: We must recognise that each nation’s values differ and their appetite for different risks will be different.
- But these differences are manageable within a larger framework.
- It is the responsibility of global leaders to guarantee the secure and safe deployment of Generative AI.
- We need to reimagine our safety assurance paradigm and build a trust framework to ensure global identity assurance and information integrity.
- Beyond regulation, we need to engineer our online safety.
- We must add rigor and responsibility to developing AI technology, enforce ethical guidelines, conduct regular audits for fairness, identify and address biases, and protect privacy and security.
QUESTION FOR PRACTICE
What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy.(UPSC 2022) (200 WORDS, 10 MARKS)
[ad_2]