[ad_1]
GS Paper 3:
Syllabus: Environment: Environmental pollution and degradation
Context:
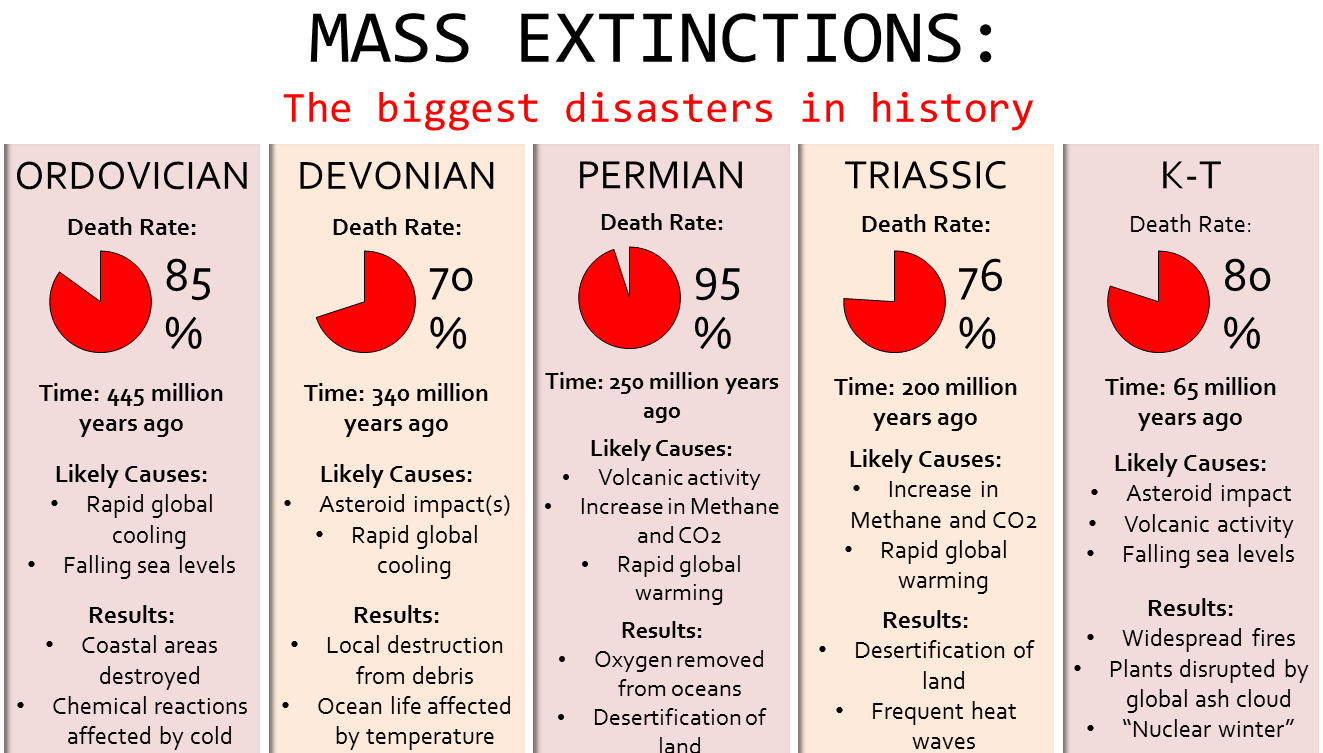
Scientists from Stanford University, warn of imminent mass annihilation of marine species similar to the Permian extinction (250 million years ago) that wiped out most lives in oceans
What is Permian extinction?
- Permian extinction (or the “Great Dying”) was caused by global warming that left ocean animals unable to breathe. Roughly 96 per cent of marine species and 70 per cent of land species went extinct.
- Permian Era: During this period, land masses collided to form the supercontinent Pangaea. The supercontinent was arid; only a few parts received rainfall round the year.
- However, the large Panthalassic Ocean, which covered much of Earth, was home to many marine species.
What led to extinction?
- Volcanic eruption: Towards the end of the era, a series of volcanic eruptions occurred in central Siberia, injecting massive amounts of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere. Then, as of now, the uncontrolled GHG emissions triggered climatic changes.
Why the studies are important now?
- Earth is undergoing a similar phase of warming: The studies predict a 2-10 degree C warming lead to many species getting extinct while other species may migrate from the tropics into polar waters.
- Ocean importance: Oceans are the planet’s largest ecosystem accounting for 95 per cent of all spaces available for life and hosting 90 per cent of the planet’s total species.
- Ocean accommodating more heat: Deep oceans are warming up. Ocean heat content is the energy accumulated by the ocean. The atmosphere has a low heat capacity compared to the ocean water, which can accommodate 1000 times more heat. So, most of the heat from GHG is moving into the ocean.
- Ocean heat content reached a record high in 2021.
Insta Links
Practice Question
Q. According to recent research, a sixth mass extinction in Earth’s history is underway and is more severe than previously feared. Discuss the magnitude, causes and remedial measures needed to halt the extinction. (15M)
| Q. The term “sixth mass extinction/sixth extinction” is often mentioned in the news in the context of the discussion of (UPSC CSE 2018) |
| a) Widespread monoculture Practices agriculture and large-scale commercial farming with indiscriminate use of chemicals in many parts of the world that may result in the loss of good native ecosystems. |
| b) Fears of a possible collision of a meteorite with the Earth in the near future in the manner it happened 65million years ago that caused the mass extinction of many species including those of dinosaurs. |
| c) Large scale cultivation of genetically modified crops in many parts of the world and promoting their cultivation in other Parts of the world which may cause the disappearance of good native crop plants and the loss of food biodiversity. |
| d) Mankind’s over-exploitation/misuse of natural resources, fragmentation/loss, natural habitats, destruction of ecosystems, pollution and global climate change. |
Answer: D
Anthropocene Extinction is an ongoing extinction event of species during the present era (known as the Holocene Epoch) due to human activity.
Q. In the context of mitigating the impending global warming due to anthropogenic emissions of carbon dioxide, which of the following can be the potential sites for carbon sequestration?
- Abandoned and uneconomic coal seams
- Depleted oil and gas reservoirs
- Subterranean deep saline formations
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
All of the site can be used for carbon sequestration
Source: Down to Earth
[ad_2]