[ad_1]
GS Paper 3
Syllabus: Infrastructure(energy, ports, roads, airports, railways etc)
Context:
- The PM is set to lay the foundation stone for include the Rs 1,400 crore multi-modal logistics park in Chennai, the Rs 5,850 crore 21-km four-lane double-decker elevated road connecting Chennai Port to Maduravoyal (NH-4), and the Rs 14,870 crore Chennai-Bengaluru Expressway project.
- The Prime Minister would dedicate to the nation four railway projects implemented at a cost of over ₹2,900crore.
- They are:
- 75 km long Madurai Theni (Railway Gauge Conversion Project)
- 30km long third railway line between Tambaram-Chengalpattu
- 115km long Ennore-Chengalpattu section
- 271km long Tiruvallur-Bengaluru section of a natural gas pipeline
Indian Railways:
- It is the world’s fourth largest rail network in the world. Railways in India
- The Indian railways employ more than 1.3 million people.
- It transports more than 90% of the coal that provides 50% of the country’s power requirement.
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) in the railways infrastructure sector.
- As per data released by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, for railways and associated sectors, the FDI inflows stood at $1.23 billion (April 2000 – March 2021).
Government initiatives:
- Rising passenger & freight traffic
- Increasing urbanization, rising incomes (both rural and urban), growing industrialization across the country along with private sector participation
- Increasing freight traffic
- Growing industrialization across the country
- Dedicated freight corridor(Six high-capacity, high-speed dedicated freight corridors)
- Diamond Quadrilateral network of high-speed rail
- Connecting major metros and growth centers of the country
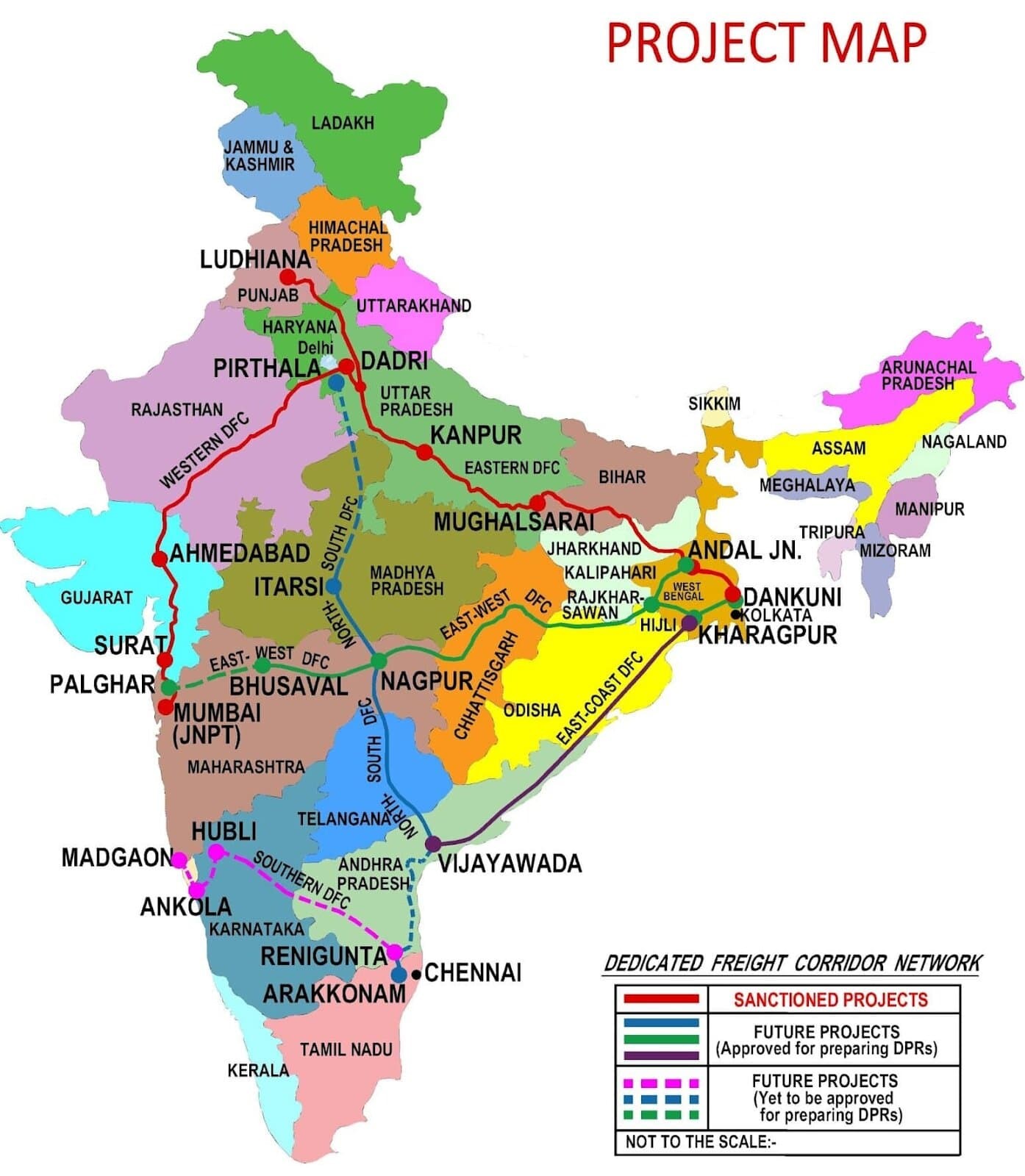
Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC):
- It is a high speed and high capacity railway corridor that is exclusively meant for the transportation of freight, or in other words, goods and commodities.
- It involves integration of better infrastructure and state of the art technology.
It consists of two arms:
Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC):
- Starts at Sahnewal (Ludhiana) in Punjab and ends at Dankuni in West Bengal.
- The EDFC route has coal mines, thermal power plants and industrial cities.
- The EDFC route covers Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal
- It is being funded majorly by the World Bank.
- The 351-km-long ‘New Bhaupur-New Khurja section’ will decongest the existing Kanpur-Delhi main line and double the speed of freight trains from 25 kmph to 75 kmph.
Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC):
- It is around 1,500-km WDFC from Dadri in Uttar Pradesh to Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust in Mumbai, touching all major ports along the way.
- It covers Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh.
- It is being funded by the Japan International Cooperation Agency.
- The Connecting Link for Eastern and Western Arm: It is under construction between Dadri and Khurja.

MultiModal Logistics Parks (MMLPs)
- The development of MMLPs at strategic locations is envisaged as a key policy measure to rationalize cost of logistics in India and improve its competitiveness.
- MMLPs serve five key functions:
- Freight aggregation and distribution
- Multimodal freight transport, integrated storage and warehousing
- Information technology support
- Value-added services.
Insta Links:
Prelims links:
New railway lines
Dedicated freight corridor
MultiModal Logistics Parks (MMLPs)
Location of different freight corridors on map
National Infrastructure Pipeline
Mains Link:
Discuss how the development of railway infrastructure will create jobs and boost the economy with examples.
[ad_2]