[ad_1]
GS Paper 3:
Topics Covered: Awareness in space.
Context:
NASA has announced the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on December 24.
- Webb, the world’s premier space science observatory, will succeed the Hubble Space Telescope, NASA’s flagship telescope that has been in service for more than three decades now.
About JSWT:
JWST is a joint venture between the US (Nasa), European (Esa) and Canadian space agencies (CSA).
- It is an orbiting infrared observatory that will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope, with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity.
- Webb was formerly known as the “Next Generation Space Telescope” (NGST) and it was renamed in 2002 after a former NASA administrator, James Webb.
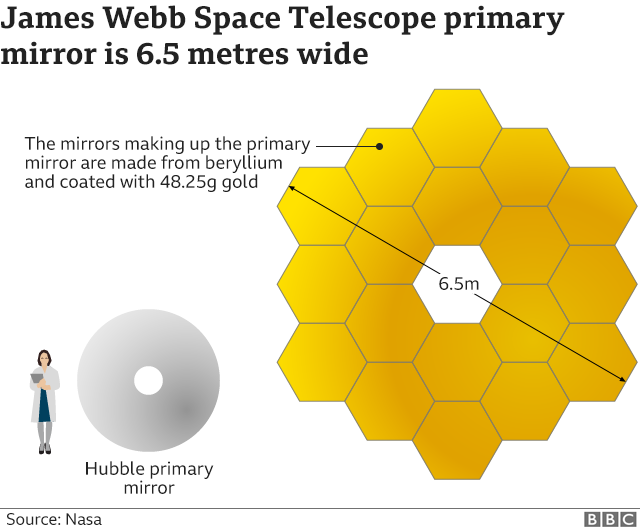
- It will be a large infrared telescope with an approximately 6.5 meter primary mirror.
Objectives and functions of the telescope:
- It will look deeper into the cosmos – and thus further back in time – than is possible with Hubble.
- It will do this with a much bigger mirror (6.5m in diameter versus 2.4m) and instruments that are tuned to the infrared.
- Scientists hope this set-up can detect the light from the very first population of stars in the Universe to switch on more than 13.5 billion years ago.
Orbit:
- The Hubble Space Telescope orbits around the Earth at an altitude of ~570 km above it.
- Webb will not actually orbit the Earth, instead it will sit at the Earth-Sun L2 Lagrange point,5 million km away.
- At the L2 point Webb’s solar shield will block the light from the Sun, Earth, and Moon which will help Webb stay cool, which is very important for an infrared telescope.
Insta Curious:
Know more about the Hubble Space Telescope here.
Sources: Indian Express.
[ad_2]