[ad_1]
GS Paper 2:
Topics Covered: Issues related to health.
Context:
Ebola resurfaces in Democratic Republic of Congo 4 months after outbreak contained.
Background:
The Ebola outbreak in 2014-2016 killed 11,300 people, mostly in Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia.
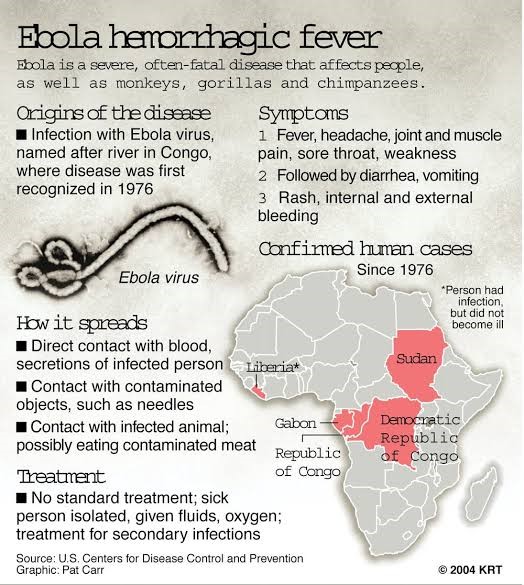
About Ebola:
Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
Transmission: The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission.
The average EVD case fatality rate is around 50%. Case fatality rates have varied from 25% to 90% in past outbreaks.
Prevention: Community engagement is key to successfully controlling outbreaks. Good outbreak control relies on case management, surveillance and contact tracing, a good laboratory service and social mobilisation.
Treatment: Early supportive care with rehydration, symptomatic treatment improves survival. There is yet no licensed treatment proven to neutralise the virus but a range of blood, immunological and drug therapies are under development.
Insta Curious:
Do you know what exactly is the Public Health Emergency of International Concern? How many PHEIC declarations have been made so far? Click here
InstaLinks:
Prelims Link:
- How is Ebola spread?
- What are zoonotic diseases?
- Differences between virus, bacteria and other pathogens.
- Where is Congo?
- Regions in Africa where Ebola outbreak was observed?
Mains Link:
Discuss how the Ebola pandemic was handled by Congo Republic.
Sources: Down to Earth.
[ad_2]