[ad_1]
NOTE: Please remember that following ‘answers’ are NOT ‘model answers’. They are NOT synopsis too if we go by definition of the term. What we are providing is content that both meets demand of the question and at the same time gives you extra points in the form of background information.
General Studies – 1
Topic: Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Reference: Indian Express
Why the question:
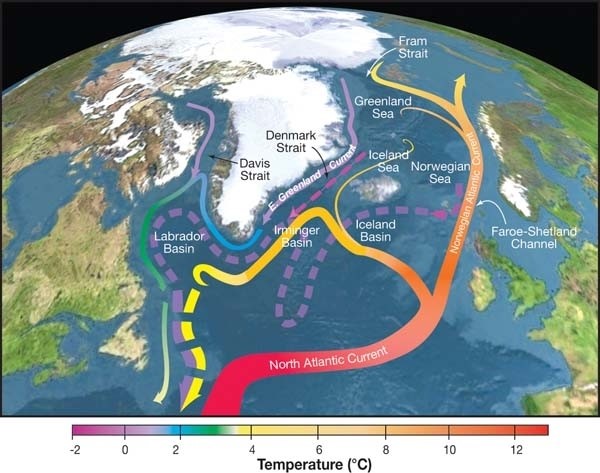
A recent study notes that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is losing its stability. Modeling studies have shown that an AMOC shutdown would cool the northern hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe.
Key Demand of the question:
Discuss the causative factors that have led to AMOC losing its stability and examine its implications on global climate systems.
Directive:
Examine – When asked to ‘Examine’, we must look into the topic (content words) in detail, inspect it, investigate it and establish the key facts and issues related to the topic in question. While doing so we should explain why these facts and issues are important and their implications.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Start with what you understand by AMOC.
Body:
The answer body must have the following aspects covered:
What causes Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation?
What is the relationship between the great ocean conveyor and the Atlantic Meridional overturn circulation? What happens if the AMOC collapses?
How does the overturning circulation in the ocean influence the global heat balance?
Discuss its implication on Global Climate system.
Conclusion:
Conclude suitably.
Introduction
Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) — which is sometimes referred to as the “Atlantic conveyor belt” — is one of the Earth’s largest water circulation systems where ocean currents move warm, salty water from the tropics to regions further north, such as western Europe and sends colder water south.
According to the recently released IPCC’s Report, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is losing its stability and is very likely to decline over the 21st century.
Body:


Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation?
- As warm water flows northwards in the Atlantic, it cools, while evaporation increases its salt content.
- Low temperature and high salt content increase the density of the water, causing it to sink deep into the ocean.
- The cold, dense water deep below slowly spreads southward.
- Eventually, it gets pulled back to the surface and warms again, and the circulation is complete.
- This continual mixing of the oceans and the distribution of heat and energy around the planet contributes to the global climate.
- Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current (AMOC) ensures the oceans are continually mixed, and heat and energy are distributed around Earth.
How does the AMOC work?
- The AMOC is a large system of ocean currents, like a conveyor belt, driven by differences in temperature and salt content – the water’s density.
- As warm water flows northwards it cools and some evaporation occurs, which increases the amount of salt. Low temperature and a high salt content make the water denser, and this dense water sinks deep into the ocean.
- The cold, dense water slowly spreads southwards, several kilometers below the surface. Eventually, it gets pulled back to the surface and warms in a process called “upwelling” and the circulation is complete.
How Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current affects?
Warming in the Indian Ocean generates additional precipitation, which, in turn, draws more air from other parts of the world, including the Atlantic. The higher level of precipitation in the Indian Ocean will reduce precipitation in the Atlantic and increase salinity in the waters.
Link between Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and the Indian Ocean:
- For thousands of years, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) has remained stable but in the last 15 years, signs show that AMOC may be slowing, which could have drastic consequences on the global climate.
- However, the rising temperatures in the Indian Ocean can help to boost the AMOC and delay slow down.
- Warming in the Indian Ocean generates additional precipitation, which, in turn, draws more air from other parts of the world, including the Atlantic.
- With so much precipitation in the Indian Ocean, there will be less precipitation in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Lesser precipitation leads to higher salinity in the waters of the tropical portion of the Atlantic — because there won’t be as much rainwater to dilute it.
- This saltier water in the Atlantic, as it comes north via AMOC, will get cold much quicker than usual and sink faster.
- The above process would act as a jump start for AMOC, intensifying the circulation.
- But if other tropical ocean’s warming, especially the Pacific’s, catches up with the Indian Ocean, the advantage of intensification for AMOC may stop.
- Moreover, it isn’t clear whether the slowdown of AMOC is caused by global warming alone or it is a short-term anomaly related to natural ocean variability.
- Slowdown of AMOC had taken place 15,000 to 17,000 years ago which caused harsh winters in Europe, with more storms or a drier Sahel in Africa due to the downward shift of the tropical rain belt.
- Alternating oceanic system patterns like ENSO also affects rainfall distribution in the tropics and can have a strong influence on weather in other parts of the world.
Impact on Global climate if AMOC collapses:
- It plays a critical role in redistributing heatand regulating weather patterns around the world.
- Colder Europe:Without a proper AMOC and Gulf Stream, Europe will be very cold.
- Rainfall decline:Modelling studies have shown that an AMOC shutdown would cool the northern hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe.
- El-Nino trigger:It can also have an effect on the El Nino.
- Cooling of Atlantic:AMOC collapse could bring about large, markedly different climate responses: a prominent cooling over the northern North Atlantic and neighbouring areas.
- Weaker thermohaline:Freshwater from melting Greenland ice sheets and the Arctic region can make circulation weaker as it is not as dense as salt water and doesn’t sink to the bottom.
Conclusion:
Climate models have long predicted that global warming can cause a weakening of the major ocean systems of the world. The AMOC decline is not just a fluctuation or a linear response to increasing temperatures but likely means the approaching of a critical threshold beyond which the circulation system could collapse leading to devastating consequences.
General Studies – 2
Topic: Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
Reference: Indian Express
Why the question:
Twenty years ago on August 6 in Erwadi in Tamil Nadu’s Ramanathapuram, a fire broke out in a thatched shelter, engulfing 43 chained people who had psychosocial disabilities.
Key Demand of the question:
Discuss in detail the importance of ensuring the dignity of persons with disability in the country.
Directive:
Elaborate – Give a detailed account as to how and why it occurred, or what is the particular context. You must be defining key terms where ever appropriate, and substantiate with relevant associated facts.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Start with the context of the question.
Body:
The answer body must have the following aspects covered:
Legal provision for the persons with disabilities.
Highlight the failure of States; Sates have failed to uphold the human rights of people with disabilities in general and those with psychosocial and intellectual disabilities in particular.
Discuss the violations of rights in private asylum.
Conclusion:
Conclude with way forward.
Introduction
Disabilities is an umbrella term, covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. An impairment is a problem in body function or structure; An activity limitation is a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; A participation restriction is a problem experienced by an individual in involvement in life situations.
As per Census 2011, in India, out of the total population of 121 crore, about 2.68 Cr persons are ‘Disabled’ (2.21% of the total population). Out of 2.68 crore, 1.5 crore are males and 1.18 crore are females. Majority (69%) of the disabled population resided in rural areas.
Body
Legal provision for the persons with disabilities:
- India ratified the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) in 2007.
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act was enacted in 2016.
- The Mental Healthcare Act (MHCA) was enacted in 2017.
Programmes/initiatives for Disabled in India
- Accessible India Campaign: A nation-wide flagship campaign for achieving universal accessibility that will enable persons with disabilities to gain access for equal opportunity and live independently and participate fully in all aspects of life in an inclusive society. The campaign targets at enhancing the accessibility of built environment, transport system and Information & communication ecosystem.
- Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme: Under the scheme financial assistance is provided to NGOs for providing various services to Persons with Disabilities, like special schools, vocational training centres, community-based rehabilitation, pre-school and early intervention etc.
- Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase / fitting of Aids and Appliances (ADIP): The Scheme aims at helping the disabled persons by bringing suitable, durable, scientifically-manufactured, modern, standard aids and appliances within their reach.
- National Fellowship for Students with Disabilities (RGMF) The scheme aims to increase opportunities to students with disabilities for pursuing higher education. Under the Scheme, 200 Fellowships per year are granted to students with disability.
- Schemes of the National Trust for the Welfare of Persons with Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation and Multiple Disabilities.
Issues and Challenges
Health:
- A large number of disabilities are preventable, including those arising from medical issues during birth, maternal conditions, malnutrition, as well as accidents and injuries.
- However, the health sector especially in rural India has failed to react proactively to disability
- Further there are lack of affordable access to proper health care, aids and appliances
- Healthcare facilities and poorly trained health-workers in rehabilitation centres is another concern.
Education:
- The education system is not inclusive. Inclusion of children with mild to moderate disabilities in regular schools has remained a major challenge.
- There are various issues such as availability special schools, access to schools, trained teachers, and availability of educational materials for the disabled.
- Further, reservations for the disabled in higher educational institutions has not been fulfilled in many instances
Employment:
- Even though many disabled adults are capable of productive work, disabled adults have far lower employment rates than the general population.
- The situation is even worse in the private sector, where much less disabled are employed
- Accessibility: Physical accessibility in buildings, transportation, access to services etc still remain a major challenge.
Discrimination/Social Exclusion:
- Negative attitudes held by the families of the disabled, and often the disabled themselves, hinder disabled persons from taking an active part in the family, community or workforce.
- Differently-abled people face discrimination in everyday life. People suffering from mental illness or mental retardation face the worst stigma and are subject to severe social exclusion.
- Inadequate data and statistics: The lack of rigorous and comparable data and statics further hinders inclusion of persons with disabilities. The major issues with collection of data and measuring disability are:
- Difficult to define disability
- Coverage: Different purposes require different disability data
- Reluctance in reporting disability as disability is considered to be a stigma in many places/societies
- Poor implementation of policies and schemes hinders the inclusion of disabled persons. Though various acts and schemes have been laid down with an aim to empower the disabled, their enforcement face many challenges.
Way Forward
Prevention
- Preventive health programs need to be strengthened and all children need to be screened at a young age.
- Kerala has already started an early prevention programme. Comprehensive New-born Screening (CNS) programme seeks early identification of deficits in infants and reduce the state’s burden of disability.
- Awareness:
- People with disabilities need to be better integrated into society by overcoming stigma
- There should be awareness campaigns to educate and aware people about different kinds of disability
- Success stories of people with disabilities can be showcased to inculcate positive attitude among people
Employment
- Disabled adults need to be empowered with employable skills
- The private sector needs to be encouraged to employ them.
- Better measurement: The scale of disability in India needs to be better understood by improving the measurement of disability.
Education
- State-wise strategies on education for children with special needs need to be devised.
- There should be proper teacher training to address the needs of differently-abled children and facilitate their inclusion in regular schools
- Further there should be more special schools and ensure educational material for differently-abled children
Access
- Safety measures like road safety, safety in residential areas, public transport system etc., should be taken up
- Further, it should be made legally binding to make buildings disabled-friendly
- Policy Interventions:
- More budgetary allocation for welfare of the disabled. There should be a disability budgeting on line of gender budget.
- Proper implementation of schemes should be ensured. There should be proper monitoring mechanisms and accountability of public funds.
Conclusion
Implementation of rights of the persons with disability needs implementation in letter and spirit and human rights-based approach.
Topic: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
Reference: The Hindu
Why the question:
India took over the Presidency of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) on August 1, from France.
Key Demand of the question:
Discuss the factors which emphasize that India deserves a permanent seat in the UNSC. Also explain the hurdles for India in achieving this goal.
Directive:
Discuss – This is an all-encompassing directive – you have to debate on paper by going through the details of the issues concerned by examining each one of them. You have to give reasons for both for and against arguments.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Start with importance of India getting permanent seat at the UNSC.
Body:
The answer body must have the following aspects covered:
India’s Pursuit for Permanent membership at UNSC and why India deserves this reward.
Trace India’s participation in the UN system from past to present.
Discuss the factors constraining India’s ambition of Permanent membership.
Explain what are the steps India is taking in pursuance of permanent membership at UNSC?
Conclusion:
Conclude with way forward.
Introduction
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations. Like the UN as a whole, the Security Council was created following World War II to address the failings of a previous international organization, the League of Nations, in maintaining world peace.
Body:
Role and Significance of UNSC:
- The Security Council is the United Nations’ most powerful body, with “primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of international sanctions, and the authorization of military action through Security Council resolutions.
- It is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states.
- Under the UN Charter, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council s decisions.
Need for reforms in UNSC:
- Regional representation
- Supporters of UNSC reform claim that there is a huge European bias in P-5 due to the presence of the United Kingdom and France including Russia.
- While regions like Latin America, Caribbean group, Arabs and Africa do not have a single permanent member. Similarly, there is a western bias in UNSC. As China is the only Asian country among the five permanent members of UNSC.
- Thus, a large chunk of the population and many different regions of the world remain unrepresented in the permanent membership of UNSC.
- It seems highly unfair that the whole continent of Africa does not have a single member in P-5 despite the fact that most of the affairs of the body concern this part of the globe only.
- So, regions like Africa and Latin America and others will have to be accommodated in the reformed UNSC.
- Changing geopolitics:
- The victors of World War II shaped the United Nations Charter in their national interests, dividing the permanent seats, and associated veto power, among themselves.
- It has been 72 years since the foundation of UNSC.
- During this period, the geopolitical realities have changed drastically, but the Council has changed very little.
- Question of Veto:
- All five permanent members of UNSC enjoy a veto power .
- Veto is a kind of negative vote by a permanent member that prevents the adoption of a proposal, even if it has received the required overall votes by the members.
- Sadly, veto power is grossly misused by the permanent members in their own national interest.
- g., out of 24 vetoes over the last 20 years, 15 have been used by the United States to protect Israel.
- This also badly affects the conduct of the business of UNSC as many important proposals involving substantive issues get blocked due to use of veto by any of the five permanent members.
- G-4 and India s quest for a permanent seat:
- In recent decades, India has been very vocal in demanding for a permanent seat in UNSC. It is also part of G-4, a group of 4 nations (India, Brazil, Germany and Japan) to lobby for permanent positions on the UNSC or at least to make the council more representative.
- Many member-states have been pledging support for our aspiration for permanent membership. Several P-5 countries have also announced their support. At present, China is the only P-5 member opposing India s bid.
- G-4 wants to expand the permanent seats in the UNSC to 10 to include 6 new members G-4 nations apart from one seat to Africa and one seat to Arabs
- Transparency and Working Methods:
- While the expansion of the Security Council has been hotly debated across the world, debate on the working methods of the Council, an equally important aspect of reform to many member states, has attracted less attention.
- It is true that UNSC has been functioning in the most non-transparent and non-consultative way.
- The undemocratic nature of UNSC within the supposedly democratic UN has compromised the overall credibility of the United Nations.
India should be given a permanent seat in the council due to:
- India in many ways is a sui generis country. It’s a country of a billion-plus, it’s a country which is a democracy, perhaps the only example in history of a billion-plus people working together in a democratic framework.
- India is the 2nd most populous nation, the 3rd largest economy in PPP terms, a responsible nuclear power and the largest democracy in the world.
- We will bring to it those values and strengths of being able to work cohesively among disparate entities.
- India is a founding member of the UN, and it has been the temporary member of the UNSC for 7 terms.
- India has provided the 2nd largest number of troops in peacekeeping missions. In Africa alone 6000 of our troops have been stationed under UN peacekeeping missions. India has argued in UN that troops contributing nations should have greater say in UNSC.
- One of the biggest issues that will confront all multilateral organisations and certainly the security council will be issues which are beyond borders.
- Issues of the global commons, whether it is in cases of public health as we are now seeing in the current pandemic, but other issues, for example, cyber [issues]. There are no regulatory mechanisms or no rules on that, and that’s another.
- A third one is issues of high seas. Again, beyond your exclusive economic zone, there is very limited understanding of what states can do and what states can’t do.
- Ungoverned spaces lead to opportunities for those who are inimical to global governance to breed, whether it is in states or it is beyond state boundaries, this has been the experience, and therefore, we as a country would like to focus on these things.
- Another area of interest would obviously be technology with a human touch. Increasingly, resilience of human beings is an important factor that all of us have been confronted with where there are disasters, can we have a more humane approach to these, etc.
Challenges:
- The US administration under Biden has continued to remain non-committal on support for India’s UNSC bid.
- The U.S. has offered qualified support for building a consensus for enlargement of the UNSC — in terms of permanent and non-permanent members. However, it said it would not support an expansion of the veto — given to the P-5, the current five permanent members: China, France, Russia, the U.K and the U.S.
- The Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group — Pakistan, South Korea, Italy and Argentina — opposes the G4 plan.
- China also opposes the bids of India and Japan.
Conclusion:
In this context, the challenges before India are many. The Security Council is one of the most important multilateral decision-making bodies where the contours of global geopolitics are often drawn. India should avoid the temptation of taking sides at a time when the Security Council is getting more and more polarised.
To serve its interests and push for its agenda of multilateralism and reforms, India should adopt value-based positions that are not transactional, aspire for the leadership of the non-permanent members of the Council and be the voice of the weaker nations.
Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Reference: The Hindu
Why the question:
The article talks about the crisis in urban employment scenario and applauds the recommendation of the parliamentary committee to have an urban employment scheme on the lines of MNREGS.
Key Demand of the question:
Present the impact of pandemic on urban employment and discuss in what way an urban job guarantee scheme is the need of the hour.
Directive:
Explain – Clarify the topic by giving a detailed account as to how and why it occurred, or what is the particular context. You must be defining key terms where ever appropriate, and substantiate with relevant associated facts.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Start with some key data.
Body:
The answer body must have the following aspects covered:
Discuss the impact of the pandemic on urban employment first; the government has not conducted a holistic survey on the way migrant workers were impacted due to pandemic induced lockdown.
Further, the PLFS highlights the job recovery, which is skewed and misleading. Most of the recovery in jobs has happened in unpaid workers category or disguised employment. Youth has been most affected, and the average wage has gone down since the pandemic.
Explain with suitable justifications as to why an urban job guarantee scheme is the need of the hour.
Conclusion:
Conclude with way forward.
Introduction
The contraction of the economy due to Covid-19 pandemic has raised concerns about the employment situation in urban areas. While the ‘Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyan’ launched in June 2020 could be an immediate relief, the ₹50,000-crore employment scheme may not be a suitable substitute for decent urban jobs.
Body
Further, the pandemic and associated policy responses (unplanned lockdown) have exposed the vulnerability of these urban jobs. Thus, for sustenance for the overall economy, there is a need for policy interventions to revive urban employment generation.
Threats to Employment
- Slowdown in Major Employment Generating Sector:The shrinking sectors that have been affected the most —construction (–50%), trade, hotels and other services (–47%), manufacturing (–39%), and mining (–23%) — are those that create the maximum jobs in the economy.
- Reverse Migration:The magnitude of economic slowdown can be exemplified by a wave of massive ‘reverse migration’ during the early phase of the lockdown whereby millions of workers returned to their home States due to a loss of livelihoods in cities.
- Vulnerable Informal Sector:According to the International Labour Organization, of the 535 million labour force in India in 2019, some 398.6 million have poor quality jobs. Further, the lockdown exposed the state of vulnerable employment in urban low-end informal jobs.
- Vulnerable employment is characterised by inadequate earnings, low productivity and difficult conditions of work that undermine the basic rights of workers.
- The high and persistent incidence of vulnerable employment are a reflection of the nature of the structural transformation process, whereby capital and labour transfer from low to higher value-added sectors.
- However, in India capital and labour are moving from low value-added activities in a sector to another sector, but not to higher value-added activities.
- This leads to a situation where a large proportion of the jobs being created is of poor quality.
- Increasing Number of Working Poor:Despite higher economic growth in recent years, working poor’s are increasing in India.
- The service sector-led growth in recent years has intensified this as there is coexistence of strong job creation in some Information and Communication Technology (ICT)-intensive services.
- However, along with a significant portion of the jobs being created in ‘traditional low value-added services, where informality and vulnerable forms of employment are dominant.
- The poor quality of jobs and high informality are key for the high level of “working poor’s”. The working poorare working people whose incomes fall below a given poverty line due to low-income jobs and low familial household income.
Way Forward
- Mobilising Localised Resources:Given the scale of urbanisation, the focus on urban employment generation programmes should be in coordination with local governments.
- This will require actors at the local level to have more resources at their disposal.
- Resource mobilisation could be enabled by the formation of local alliances, involving elected representatives, trade unions, entrepreneurs and community groups
- This can also be the key to solving other problems faced by cities.
- Localised Employment-Intensive Investment Policies:A major local initiative would be to design and implement employment-intensive investment policies. In this pursuit:
- Local enterprise formation needs to be an integral part of the strategy, with converging interests for workers and entrepreneurs on issues related to technology and productivity enhancement.
- Also, Small and micro enterprises which are the fulcrum of industrialisation, need extra support to balance the interests between labour and capital as neither have collective bargaining powers.
- Prioritising Urban Infrastructure:There is a need to prioritise urban infrastructure as it accounts for a large share of total investments in the overall economy.
- A labour- intensive approach to building municipal infrastructure can be a cost-effective alternative to capital intensive-approach as wage rates are low.
- Infrastructure investments would spur employment, generate earnings and contribute to small enterprise formation.
- Construction of low-cost housing is another activity that can be carried out using labour-intensive methods, while yielding substantial collateral benefits for urban dwellers.
- Launching of Urban Employment Scheme:There is need for immediate launch of an urban employment scheme oriented toward building large-scale medical, health and sanitation infrastructure in cities and towns across India.
- MGNREGAcan be expanded for urban areas, both in terms of increasing the budgetary allocations and the guaranteed minimum number of days of work.
- Other immediate employment generation can be to expand networks of essential services as a part of welfare interventions of State and local governments.
- Increase Incentives to Reduce Migration:Focusing on rural development to increase employment opportunities in rural areas and to enhance the provision of services like education, health, electricity and water and sanitation services are effective means to control rural to urban migration.
Conclusion
Given the economic contraction, there is a need to generate more jobs and reduce vulnerabilities by providing decent wages & job security in urban areas. Thus, the present crisis calls for a multi-pronged strategy to tackle the issue of urban jobs.
General Studies – 3
Topic: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Reference: The Hindu
Why the question:
The Plastic pact model to address plastic pollution is now being brought to India by CII and WWF India.
Key Demand of the question:
Answer must present a detailed analysis of the plastic waste issue and solutions offered by plastic pact model.
Directive:
Discuss – This is an all-encompassing directive – you have to debate on paper by going through the details of the issues concerned by examining each one of them. You have to give reasons for both for and against arguments.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Briefly present the menace of plastic wastes globally.
Body:
The answer body must have the following aspects covered:
Why plastic waste needs to be managed? – A 2019 report by the Center for International Environment Law suggest that by 2050 Greenhouse Gas emission from plastic could reach over 56 gigatonnes. Similarly, the report Closing the Plastics Circulatory gap by Google suggest that without a large scale intervention we will be mismanaging more than 7.7 billion metric tonnes of plastic waste globally in the next 20 years.
Explain in what way Plastic waste is a key societal challenge.
Discuss the challenges and opportunities of plastics management.
Conclusion:
Conclude with solutions.
Introduction
The current plastics system demands fundamental change in which research and innovation, enabled and reinforced by policymaking, play a crucial role. By moving towards a circular economy, the benefits of plastics can be harnessed, while achieving better economic, environmental, and social outcomes.
India, as part of her green initiatives has decided that the India Plastics Pact, the first in Asia, will be launched in September at the CII Annual Sustainability Summit. It aims to address the plastic waste problem by an in-depth analysis of the plastic waste issue and offers solutions offered as part of the plastic pact model.
Body
Plastic pacts model:
- The Plastics Pacts are business-led initiatives and transform the plastics packaging value chain for all formats and products.
- The Pacts bring together everyone from across theplastics value chain to implement practical solutions.
- Integral to the Pact’s framework is the involvement of the informal waste sector crucial topost-consumer segregation, collection and processing of plastic waste.
- All Pacts unite behind four targets:
- To eliminate unnecessary and problematic plastic packaging through redesign and innovation.
- To ensure all plastic packaging is reusable or recyclable.
- To increase the reuse, collection, and recycling of plastic packaging.
- To increase recycled content in plastic packaging.
- Plastic pact modelwhich is now implemented in number of countries such as UK, South Africa, Australia offers such a solution which is multi-pronged, systemic, and large scale, to create a visible impact.
Challenges and opportunities posed by Plastic waste:
- A 2019 report by the Center for International Environmental Law suggests that by 2050, greenhouse gas emissions from plastic could reach over 56 gigatonnes, 10-13% of the remaining carbon budget.
- As much as 3.3 million metric tonnes of plastic waste was generated in India in 2018-19, according to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) report 2018-19. This roughly translated to 9,200 tonnes a day (TPD).
- The total municipal solid waste generation is 55-65 million tonnes; plastic waste is approximately 5-6 per cent of the total solid waste generated in the country.
- A 2021 report commissioned by Google, Closing the Plastics Circularity Gap, suggests that unless large-scale global interventions are made, we should expect to mismanage more than 7.7 billion metric tonnes of plastic waste globally over the next 20 years.
- However, viewed from the angle of livelihoods, post-consumer segregation, collection and disposal of plastics make up about half of the income of 1.5- 4 million waste-pickers in India.
- Hence, India also needs a long terms solution for its plastic waste problem. And for India, the solution must be
How Plastic pacts will help?
- Economic advantage:It can be expected to boost demand for recycled content, investments in recycling infrastructure, jobs in the waste sector, and beyond.
- Support EPR framework:The Pact will support the Extended Producer Responsibility framework of the government and improve solid waste management as envisioned in the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
- The India Plastics Pact focuses on solutions and innovation.
- Plastic production and management development: The Pact will encourage the development and maturing of the entire plastics production and management ecosystem.
- Drive circulatory of plastic:Apart from benefits to society and economy, delivering the targets will drive the circularity of plastics and help tackle pollution.
Conclusion
India Plastic Pact focuses on innovation and solutions. It ensures accountability trough setting up of targets and data reporting. While the India Plastics Pact will be active in India, it will link globally with other Plastics Pacts which is expected to benefit businesses especially MSME’s.
Topic: Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Reference: Indian Express
Why the question:
Last week, Parliament passed a new law that will bring uniformity in the rules and regulations governing inland waterways and navigation on them.
Key Demand of the question:
Analyse the features of the Inland Vessels Bill 2021 in the development of Inland waterways in India.
Directive:
Analyze – When asked to analyse, you have to examine methodically the structure or nature of the topic by separating it into component parts and present them as a whole in a summary.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
The Inland Vessels Bill, 2021 replaces the century-old Inland Vessels Act, 1917. One of the key things the new Bill seeks to do is bring all inland waterways in India and movement of vessels on them for any purpose under a central regulatory regime.
Body:
The Inland Vessels Bill, 2021 replaces the Inland Vessels Act, 1917. It seeks to bring all inland waterways in India and movement of vessels on them for any purpose under a central regulatory regime.
The Bill defines mechanically propelled vessels as ships, boats, sailing vessels, container vessels, and ferries. The Centre will frame classification, standards of design, construction, and crew accommodation.
Discuss its contributions to Inland waterways.
Conclusion:
Conclude with importance.
Introduction
The Inland Vessels Bill, 2021 has been passed by the Lok Sabha in July 2021. It replaces the century-old Inland Vessels Act, 1917. The inland waterways network spans close to 15,000 km across rivers, channels, backwaters, creeks etc.
India has constantly been taking up initiatives for the development of waterways and water transport in the country like the Sagarmala project, Jal Vikas Marg Project etc. The Inland Vessels Bill 2021 further propels the Inland water transport potential of India.
Body
Objectives of Inland Vessels Bill, 2021:
- This Bill will promote economic and safe transportation and trade of inland waterways and bring uniformity in the application of the law.
- It is aimed at developing India’s inland waterways as a viable, thriving mode of transport, especially for cargo.
- It also aims in reducing the water pollution caused by these inland vessels as this bill directs the Central Government to designate a list of chemicals, substances, etc. as pollutants

Key Features of the Inland Vessels Bill, 2021
- Promotes cooperative federalism:
- This will be a unified law for the entire countryand will supplant the separate rules framed by the States
- Vast expanse of inland water:
- It enlarges the definition of ‘inland waters’, by including tidal water limit and national waterwaysdeclared by the Central Government.
- A total of 4000 km of inland waterways have been operationalised.
- The definition will further increase the expanse of inland water.
- Registration:
- The certificate of registration granted under the proposed law will be deemed to be valid in all States and Union Territories, and there will be no need to seek separate permissions from the States
- The Centre will frame classification, standards of design, construction, and crew accommodation.
- Construction or modification will require approval of a designated authority.
- All such vessels are to be registered with respective states or Union Territories.
- Centralised database:
- As per the bill, a central database will be maintainedthat shall record each vessel’s details like its registration and crew, all on an electronic portal
- Differentiation of vessels:
- The Bill defines mechanically propelled vessels as ships, boats, sailing vessels, container vessels, and ferries.
- The vessels which are mechanically propelled will have to register themselves mandatorily as per the bill, and the non-mechanically propelled vessels willalso have to compulsorily register themselves at district, taluk or panchayat or village level
- Pollution control:
- It also deals with pollution control measures of Inland Vessels. This Bill directs the Central Government to designate a list of chemicals, substances, etc. as pollutants.
- The new law empowers the Centre to prescribe what kind of pollutants and sewage vessels and can discharge, and how much.
- Inland Vessels Fund:
- The Bill envisages maintaining a fund, which will be used for emergency preparedness, checking pollution and boosting navigation. The fund will source from state governments schemes, sale of cargo and wreck and contribution from stakeholders.
- Response during distress:
- The new law mandates that if any distress or SOS signal is sent out by the master of a vessel, any other vessel nearby must respond — much like maritime custom and rules on sea.
- If the master of a nearby vessel fails to come for help, he or she will be fined up to Rs 10,000 unless they failed to provide assistance on some specified grounds.
- In case of accidents, the nearest police station is to be involved for inquiry and action.
Way forward:
- Strengthening public-private partnership has the key role to play in developing the inland waterways sector.
- Private players can undertake terminal development, cargo and passenger handling, and building low-draft vessels and related repair facilities.
- Measures should be taken to develop basic infrastructure, address technological bottlenecks and maintenance of rivers to ensure year-round navigability
- Measures should be taken to taken to ensure availability of seamless, multimodal last-mile connectivity to and from hinterland to reduce trans-shipment cost and make inland water transport economically more viable
- Cargo transport through inland waterways should be incentivised. Following measures can be taken:
- The Government can mandate/incentivise industries in the proximity of national waterways to use this mode for a portion of their shipments.
- the government can promote industrial corridors along riverbanks and foster waterways-based industrialisation.
- Higher road taxes can be levied on transportation of coal and inflammable material over longer distances
- The government should develop passenger terminal development, offer financial support to ferry operators to improve safety, and facilitate insurance coverage to boost passenger transport
- Measures should be taken to promote river tourism in states like Assam and Kerala
- Keeping in mind the concerns, it is important to assess the environmental and social impact of development of inland waterways and associated infrastructure to reduce the negative externalities.
Topic: role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security
Reference: The Hindu
Why the question:
The article tries to understand and bring out misinformation against women.
Key Demand of the question:
One is expected to present a detailed analysis as to how a healthy democracy like India should empower and protect the entire society.
Directive:
Comment– here we have to express our knowledge and understanding of the issue and form an overall opinion thereupon.
Structure of the answer:
Introduction:
Start with recent incidences of misinformation with respect to gender.
Body:
Sexism and online harassment prevent women from taking vocal stands and hinder progress. Men are at the centre of this disinformation. Men manufacture such false news and also fall for it.
They also indulge in disinformation to keep propaganda, including political propaganda alive. Such misinformation has been empowered by the arrival of the internet.
Discuss the major issues with some examples.
Suggest what needs to be done.
Conclusion:
Conclude with the need to promote a more democratic society, because a healthy democracy is participatory and promotes gender inclusiveness.
Introduction
Today ‘s era is the era of internet whose presence and active involvement has swiftly and widely spread the ideologies for women empowerment. Internet has become the agent of social change which helped and supported women‘s empowerment in various aspects such as mobilizing attention of glocal community towards women‘s rights and challenges, discrimination and stereotypes across the globe. Internet has given a platform to discuss issues and challenges of women through blogs, chats, online campaign, online discussion forums, and online communities which is mostly not disseminated or propagated by mainstream media.
Body
Internet has empowered the society:
- Online Banking: In the world we live today, the role of Internet has tremendously grown. In the field of online banking, the advantages of internet are of pivotal importance. Earlier, there used to be manual banking work. It was quite difficult to handle banking and transaction online. Now, with the help of Internet it has been made quite easier to send and receive payments anywhere in the world. It has brought many positive economic impacts on our society.
- Online Trade & E commerce: E-commerce is gaining popularity across the world. It is only because of Internet that doing business has become quite easier. Online buying and selling has become quite flexible. Online trade has changed the fortunes of millions of people across the world. It has revolutionized the social life. Therefore, it is another important social impact of internet on our lives.
- Faster Connectivity: Due to Internet, the connectivity has become much faster. The distances have disappeared. The world has become global. It is quite easy to connect with each other. The virtual world has made it possible for us to get in touch easily with each other. The world has become a global village where the knowledge, ideas, information and everything flows quite easily from one place to another. It has the great benefits for society.
- Creation of More Jobs & More Income Opportunities: In Old times, the economy used to be limited and isolated. But with the advent of Internet the industries and world economies have come closer to each other. Thanks to Internet, millions of new jobs are being created. The economic advantages of internet for society have been witnessed. Millions of People are changing their lives with the help of Internet. This is one of the greatest benefit of Internet for society.
- Spread of Education and Awareness: Internet has completely changed the system of education. Earlier there used to be the traditional and limited education system. Education has spread quickly via online learning. The online education system via internet has dramatically reduced the cost of education. It has become easily accessible and affordable. With the help of online videos platforms, teaching models and multiple audio, video and visual study material, the education and awareness has been spreading very fast. It is again one of the greatest social benefit of Internet for our lives.
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence and machine learning has completely changed the scope and future of computer education. Artificial intelligence is proving quite beneficial for society. It is useful in every walk of life including in education, health, economy, trade, industry and in medial field. This great social benefit is again due to internet.
- Role of Internet and Informational Technology in Medical and Health Field: We have studied that, in old times, millions of people suffered and died only because of disease that are commonly curable today. The diseases like Malaria, Typhoid and others had caused millions of people die in the past. Thanks to modern technology of today we have the cures of these diseases easily available. The medical field has greatly progressed because of Internet connectivity and information technology.
Challenges faced by women on Internet

Online abuse of women:
- To add to the gender disparity in access to the internet, women are having to face online abuse.
- Though even men are targeted online, the attacks faced by both sexes are vastly different. Misinformation/disinformation targets men and women differently. A large number of young women and girls have experienced online abuse and they are more vulnerable to such abuse.
Forms of online abuse:
- According to a recent report of the Special Rapporteur on violence against women for the United Nations Commission on Human Rights, online abuse can involve a variety of activities.
- It can include actions like bullying, trolling, cyberstalking, defamation and hate speech, public shaming, and identity theft and hacking, sexual harassment and threats of sexual violence, or the sharing of intimate images and videos without permission.
Gendered disinformation:
- Women are more prone to gendered disinformation.
- Misinformation and sexism have a symbiotic relationship. Misinformation piggybacks on sexism to discredit vocal women and sexism uses misinformation to reinforce patriarchal norms.
Inter-sectional challenges:
- Misinformation like other forms of abuse and discrimination has inter-sectional challenges.
- Organised disinformation and sexism intersect with Islamophobia, casteism, religious bigotry and other forms of discrimination. This only increases the impact on women from such vulnerable sections.
Vulnerability of women even in high positions:
- Even women in high positions are not spared from online abuse.
- A 2020 report by Amnesty International noted a considerable number of female politicians receiving hateful mentions on social media platforms like Twitter. A substantial proportion of them was either sexist or misogynistic.
- Women journalists are at great risk of being under such attacks on their social media platforms. A recent report by UNESCO on online harassment faced by women journalists says that political actors instigate and fuel online violence campaigns against women journalists.
- This is indicative of the extent of online abuse against women and girls and their vulnerability to it.
Measures needed:
- Government level:
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal shall be designated as the national portal under-reporting requirements in the POCSO Act in case of electronic material
- Union Government shall be empowered through its designated authority to block and/or prohibit all websites/intermediaries that carry child sexual abuse material
- Law enforcement agencies should be permitted to brake end to end encryption to trace distributors of child pornography.
- A cyber-crime portal was launched in 2018 to enable citizens to report obscene contents.
- Cyber police stations and cyber-crime cells were set up in each state for reporting and investigating cybercrime cases.
- Use of Artificial intelligence:
- Tools can be developed which can analyse the behaviour of every internet user. So, it can help prevent the user from falling into cyber bullying.
- Developing some mobile applications that can alert parents if the child is under threat of cyber bullying.
- Prevent malware attacks by tying up with antivirus agencies.
- Multipronged approach to handle cases:
- Need to handle the cases of cyber bullying through multipronged approach such as counselling through Psychiatrist, approaching police, etc.
Way forward:
- Social media platforms have moral obligations to safeguard their users.
- They must strive towards ensuring transparent and efficient reporting systems so that people can use them to curb cyberbullying.
- Making social media platforms accountable
- Countermeasures against online trolling must be encompassed within the women empowerment policies
- Online women-specific crime reporting unit must be set up for quicker disposal for complaints regarding targeted harassment of women users of social media.
- Increasing political representation of women for removing societal inequality, discrimination and misogyny
- The cybercrimes in social media platforms are mainly addressed under the IPC provisions that deal with conventional offences like sexual harassment, privacy violation etc.
- They are largely inefficient in dealing with techno-motivated crimes, which have more impact on victims than those traditional offences due to the lack of justice.
- Therefore, the cybercrimes under the IT Act must be repealed and IPC must be modified to cover all cybercrimes, including those currently covered under the IT Act.
Conclusion:
As part of a knowledge society in the new media era, Internet considerably contribute to women empowerment by offering information and education that presents women users with strategies offering better informed decision making from anywhere and everywhere which may not be possible otherwise.
[ad_2]