[ad_1]
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Dalit Bandhu Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions and GS-III – Entrepreneurship
In news The programme will be launched on a pilot basis in Huzurabad, Telangana on August 16.
What is Dalit Bandhu Scheme?
- Dalit Bandhu is the latest flagship programme of the Telangana government.
- It is envisioned as a welfare scheme for empowering Dalit families.
- The scheme shall enable entrepreneurship among Dalits through a direct benefit transfer of Rs 10 lakh per family who have no bank guarantee to start their businesses.
- Telangana CM Stated that “The financial assistance given by the government through Dalit Bandhu is free. This is not a loan. There is no need to repay it. There is no chance of any middlemen in this. Eligible beneficiaries will get the assistance in their bank accounts”.
- Apart from monetary assistance, the government plans to create a corpus called the Dalit Security Fund permanently to support the beneficiary in the event of any adversities.
- This fund will be managed by the district collector concerned, along with a committee of beneficiaries.
- A minimum amount will be deposited by the beneficiary towards this fund.
- The beneficiary would be issued an identity card with an electronic chip, which will help the government monitor the progress of the scheme.
- Once implemented on the ground, this is going to be the biggest cash transfer scheme in the country.
- The funds allocated for the scheme would be over and above the funds earmarked for the SC Sub Plan.
- The state government will also pursue the scheme with the Centre for nationwide implementation.
News Source: TH
India assumes UNSC Presidency
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news India has assumed the Presidency of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
- Taking over the Presidency from France, this is India’s first Presidency during its 2021-22 tenure as a non-permanent member of Security COuncil.
- India’s two-year tenure as a non-permanent member began in January 2021.
- It will again take over as the President of the Council in December 2022.
What will be India’s agenda during its Presidency?
- During its Presidency, India will be organizing high-level signature events in three major areas:
- Maritime security
- Peacekeeping and
- Counterterrorism
About United Nations Security Council
- The UNSC is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations
- It is charged with the maintenance of international peace and security.
- Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of international sanctions, and the authorization of military action through Security Council resolutions.
- It is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states.
- The Security Council consists of fifteen members.
- Permanent members (P5): Russia, UK, France, China, and USA
- These permanent members can veto any substantive Security Council resolution, including those on the admission of new member states or candidates for Secretary-General.
- The Security Council also has 10 non-permanent members, elected on a regional basis to serve two-year terms.
- The body’s presidency rotates monthly among its 15 members.
News Source: TH
Clinical trials of ‘Ashwagandha’ soon
Part of: Prelims and GS -II- International Relations; Health
In news The Ministry of Ayush has collaborated with the U.K.’s London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) to conduct a study on ‘Ashwagandha’ for promoting recovery from COVID-19.
- Clinical trials of ‘Ashwagandha’ will be conducted on 2,000 participants in three U.K. cities — Leicester, Birmingham and London
- This is the first time the Ministry of Ayush has collaborated with a foreign institution to investigate its efficacy on COVID-19 patients.
- The successful completion of the trial could be a major breakthrough and could give scientific validity to India’s traditional medicinal system.
What is ‘Ashwagandha’?
- ‘Ashwagandha’ (Withania somnifera or AG), commonly known as ‘Indian winter cherry’, is a traditional Indian herb that boosts energy, reduces stress and makes the immune system stronger.
- It is classified as an adaptogen, which means that it can help the body to manage stress.
- Ashwagandha also boosts brain function and lowers blood sugar, and helps fight symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Ashwagandha has shown clinical success in treating both acute and chronic rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain and damage throughout your body.
- An autoimmune disease is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body.
- It is an easily accessible, over-the-counter nutritional supplement in the U.K. and has a proven safety profile.
- The positive effects of ‘Ashwagandha’ have been observed in long COVID-19,
- Recently, a number of randomised placebo-controlled trials of AG in humans in India had demonstrated its efficacy in reducing anxiety and stress, improving muscle strength and reducing symptoms of fatigue in patients treated for chronic conditions.
News Source: TH
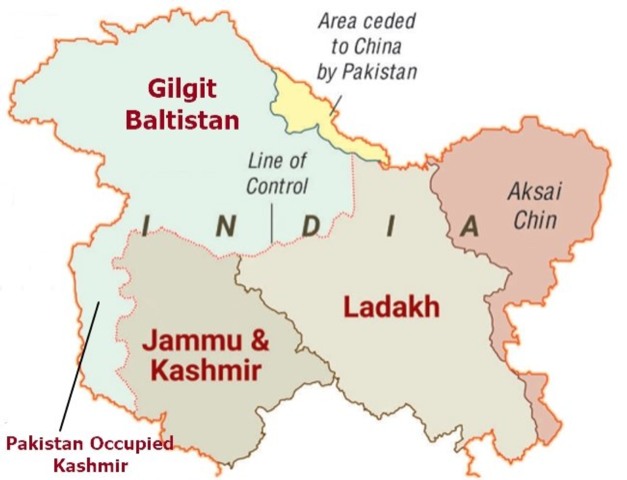
Pakistan to grant new status to Gilgit-Baltistan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations; Health
In news Pakistani authorities have finalised a law to award provisional provincial status to strategically located Gilgit-Baltistan.
- Under the proposed law, the Supreme Appellate Court (SAC) of Gilgit-Baltistan may be abolished and the region’s election commission is likely to be merged with the Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP).
- G-B will become the fifth province of Pakistan. Currently, Pakistan has four provinces – Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, and Sindh.
- This elevation will lead to adequate representation from the province on all constitutional bodies, including the National Assembly and the Senate.
India’s Stand
- India has clearly conveyed to Pakistan that the entire Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, including the areas of Gilgit and Baltistan, are an integral part of the country by virtue of its fully legal and irrevocable accession.
- India maintains the Government of Pakistan or its judiciary has no locus standi on territories illegally and forcibly occupied by it (during 1948 war).
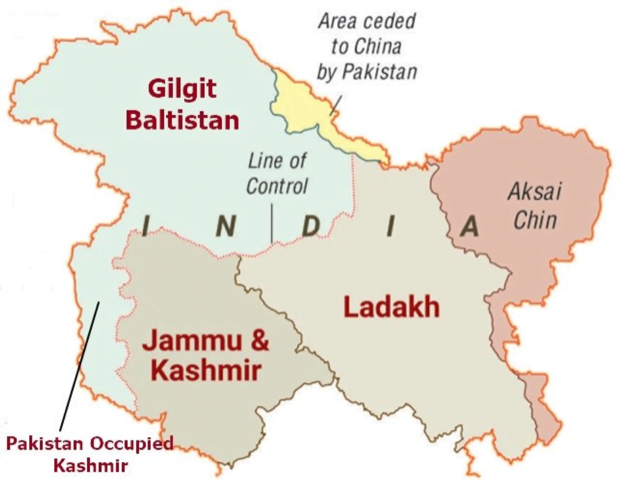
About Gilgit-Baltistan
- The region is claimed by India as part of the erstwhile princely state of Jammu & Kashmir as it existed in 1947 at its accession to India.
- Gilgit-Baltistan is the northernmost territory administered by Pakistan, providing the country’s only territorial frontier, and thus a land route, with China, where it meets the Xinjiang Autonomous Region.
- Until now, Gilgit-Baltistan was governed as a separate entity by Pakistan and not as a part of Pakistan occupied Kashmir (PoK).
- Islamabad had hesitated to declare it a province of Pakistan because of its claim that J&K is disputed territory and its future must be decided by a plebiscite among all its inhabitants.
- One of the most mountainous regions in the world that is rich with mines of gold, emerald and strategically important minerals, and known for its extraordinary scenic beauty, diversity and ancient communities and languages, Gilgit-Baltistan is largely an underdeveloped region.
- It is home to K-2, the second tallest mountain in the world.
- Tourism remains restricted by many factors, including military hostility, though the region has some of the ancient Buddhist sculptures and rock edicts.
- It is also home to an old Shia community, which often finds itself subjected to persecution in Pakistan’s urban centres.
- The water-rich region’s biggest hydroelectricity project is the Diamer-Bhasha dam, which was launched in July 2020.
News Source: TH
ADIP Scheme and Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news A ‘Samajik Adhikarita Shivir’ for distribution of aids and assistive devices to ‘Divyangjan’ under the ADIP Scheme and to Senior Citizens under the ‘Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana’ was organised by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India.
What is Assistance to Disabled persons for purchasing/fitting of aids/appliances (ADIP) scheme?
- Objective: To assist the needy disabled persons in procuring durable, sophisticated and scientifically manufactured, modern, standard aids and appliances that can promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation, by reducing the effects of disabilities and enhancing their economic potential.
- Implementation: Through implementing agencies such as NGOs, National Institutes under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment and ALIMCO (a PSU that manufactures artificial limbs).
- Eligibility: A person satisfying all the following conditions are eligible:
- Indian citizen of any age
- Has 40% disability or more (must have the requisite certificate)
- Monthly income, not more than Rs.20000.
- In the case of dependents, income of parents/guardians should not exceed Rs.20000.
- Must not have received assistance during the last 3 years for the same purpose from any source. However, for children below 12years of age, this limit would be one year.
What is Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana?
- Coverage: Senior Citizens, belonging to BPL category and suffering from any of the age-related disability/infirmity Low vision, Hearing impairment, Loss of teeth and Locomotor disability.
- Assistance is provided in the form of distributing Assisted-living devices which can restore near normalcy in their bodily functions, overcoming the disability/infirmity manifested free-of-cost.
- Funding: Central Sector Scheme. The expenditure for implementation of the scheme will be met from the “Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund “.
- Beneficiaries in each district will be identified by the State Governments/UT Administrations through a Committee chaired by the Deputy Commissioner/District Collector. As far as possible, 30% of the beneficiaries in each district shall be women.
News Source: PIB
Operation Blue Freedom: Team CLAW
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Issues related to Disability
In news Recently, the Government of India has accorded sanction to Team CLAW to lead a team of people with disabilities to scale Siachen Glacier and create a new world record for the largest team of people with disabilities.
- This is the land world record expedition part of ‘Operation Blue Freedom Triple World Records’ being undertaken.
- Triple Elemental World Records is a series of world records being attempted by the team in 2021 of collectives of people with disabilities achieving great feats on land, in air and underwater.
What is Team CLAW and Operation Blue Freedom?
- Team CLAW: Team CLAW (Conquer Land Air Water) is a team of ex-Indian Special Forces commandos.
- Generally, all are either from Indian Army Para Commandos or the Naval Marine Commandos, also known as the MARCOS.
- These veterans have multiple specialisations such as skydiving, scuba diving, mountaineering, etc.
- The initiative was taken by Major Vivek Jacob, a Para (Special Forces) officer.
- Operation Blue Freedom: It is a social impact venture aimed at rehabilitating people with disabilities through adaptive adventure sports.
- Aim: To shatter the common perception of pity, charity and inability associated with people with disabilities and recreate it to one of dignity, freedom and ability.
- Focus: To ‘design and implement sustainable large-scale employment solutions’ for people with disabilities
- It was launched in 2019 by Team CLAW.
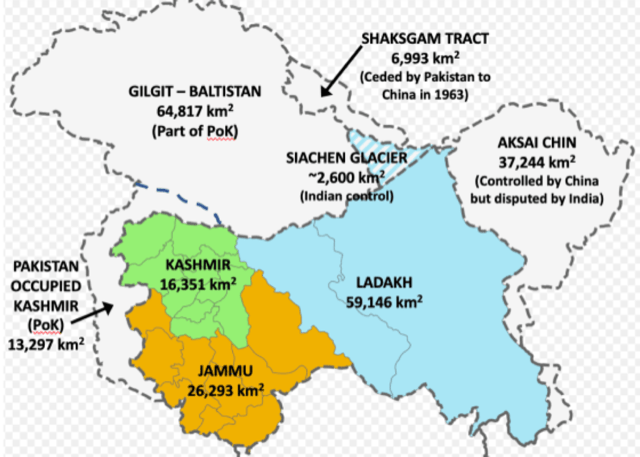
What is Siachen Glacier?
- The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends.
- It is the Second-Longest glacier in the World’s Non-Polar areas.
- Fedchenko Glacier, located in Yazgulem Range, Tajikistan is the Longest glacier in the World’s Non-Polar areas.
- The Siachen Glacier lies immediately south of the great drainage divide that separates the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent in the extensively glaciated portion of the Karakoram sometimes called the “Third Pole”.
- It is part of Ladakh
- It is the world’s highest battlefield.
- The entire Siachen Glacier has been under the administration of India since 1984 (Operation Meghdoot).
News Source: TH
Biotech-PRIDE
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Biotechnology
In news Recently, Biotech-PRIDE (Promotion of Research and Innovation through Data Exchange) Guidelines was released by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Further, a website of Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) was also launched.
About Biotech-PRIDE Guidelines
- These guidelines envisage to bridge other existing biological datasets/data centres with the IBDC, which will be called Bio-Grid.
- This Bio-Grid will be a National Repository for biological knowledge, information and data.
- Also, Bio-Grid will be responsible for enabling its exchange, developing measures for safety, standards and quality for datasets and establishing detailed modalities for accessing data.
- These guidelines will be implemented through Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC).
- Currently, India ranks number 4 amongst the top 20 countries contributing biological databases.
Important Schemes and Policies Regarding Biotech
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
How will consumers benefit from ‘Right to Repair’?
Context: On July 21, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) voted unanimously to make a push for the right of consumers to repair their electronic devices. All five FTC Commissioners voted in favour of a policy that seeks to know whether companies that are making it tougher for people to repair are violating antitrust laws
This decision would help “root out unlawful repair restrictions” and move forward with “new vigour” against violators.
What happens in the era of mobile computing?
- In the pre-smart phone era, certain issues in a mobile device could be repaired by the user themselves.
- It wasn’t the case any more now. For ex: To get an Apple product fixed, a buyer has to take it only to an authorised dealer as any warranty on the product would become null and void if they opened the back of the smartphone.
- Even after taking the device to an authorised store, the cost of repair could be high. Also, lack of Apple support makes such external repairs risky.
- Hardware is only one part of the problem.
- In 2018, an Australian court ordered Apple to pay a penalty of Australian $9 million ($6.6 million) after it told its customers it wouldn’t do free repairs for devices that stopped working due to a software glitch.
- Apple is a microcosm of the consumer tech industry itself.
- From home appliances to tractors, an increasing number of consumer products are run on software, and a technical glitch can only be fixed by an authorised technician.
- Tinkerers and large corporations are fighting to solve the issue of who owns the information needed to fix a device.
- Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in the U.S. are taking refuge under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), 1998, where it is illegal to break a digital lock embedded in a product.
Why is the movement important?
- A consortium of advocacy groups is trying to push repair-friendly laws in the U.S. and break the DMCA stronghold.
- The Repair Association’s premise is that consumers can maintain their products, provided tools and information on fixing is available to them.
- Since its founding in 2013, the group has put several ‘Right to Repair’ proposals in US state legislatures. The FTC vote is a major win for the group.
- The proposed legislation requires consumer electronics-makers to provide tools and information necessary to repair electronic products.
- This could change how companies operate by making them provide information and parts to unofficial repair centres, and, in the process, reduce costs for the consumer.
What is the stand of the tech giants?
- Tech giants have been lobbying against the legislation, citing security concerns.
- TechNet, a trade group representing large tech firms, said allowing unvetted parties to access sensitive information, tools and components would “jeopardise safety of consumers’ device and put consumers at risk of fraud”.
- But the FTC had earlier concluded that there was scant evidence to support the companies’ claim for restricting repair.
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
e-RUPI
Context: Taking the first step towards having a digital currency in the country, PM Modi will launch an electronic voucher based digital payment system “e-RUPI”.
The platform, which has been developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the National Health Authority, will be a person-specific and purpose-specific payments system
How will e-RUPI work?
- e-RUPI is a cashless and contactless digital payments medium, which will be delivered to mobile phones of beneficiaries in form of an SMS-string or a QR code.
- This will essentially be like a prepaid gift-voucher that will be redeemable at specific accepting centres without any credit or debit card, a mobile app or internet banking.
- e-RUPI will connect the sponsors of the services with the beneficiaries and service providers in a digital manner without any physical interface.
How will these vouchers be issued?
- The system has been built by NPCI on its UPI platform, and has onboarded banks that will be the issuing entities.
- Any corporate or government agency will have to approach the partner banks, which are both private and public-sector lenders, with the details of specific persons and the purpose for which payments have to be made.
- The beneficiaries will be identified using their mobile number and a voucher allocated by a bank to the service provider in the name of a given person would only be delivered to that person.
What are the use cases of e-RUPI?
- According to the government, e-RUPI is expected to ensure a leak-proof delivery of welfare services.
- It can also be used for delivering services under schemes meant for providing drugs and nutritional support under Mother and Child welfare schemes, TB eradication programmes, drugs & diagnostics under schemes like Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, fertiliser subsidies etc.
- The government also said that even the private sector can leverage these digital vouchers as part of their employee welfare and corporate social responsibility programmes.
What is the significance of e-RUPI and how is it different than a digital currency?
- The government is already working on developing a central bank digital currency and the launch of e-RUPI could potentially highlight the gaps in digital payments infrastructure that will be necessary for the success of the future digital currency.
- In effect, e-RUPI is still backed by the existing Indian rupee as the underlying asset and specificity of its purpose makes it different to a virtual currency and puts it closer to a voucher-based payment system.
- Also, the ubiquitousness of e-RUPI in the future will depend on the end-use cases.
- On the other hand, central bank digital currency or CBDC — digital currencies issued by a central bank that generally take on a digital form of the nation’s existing fiat currency
Are there global examples of a voucher-based welfare system?
- In the US, there is the system of education vouchers or school vouchers, which is a certificate of government funding for students selected for state-funded education to create a targeted delivery system. These are essentially subsidies given directly to parents of students for the specific purpose of educating their children.
- In addition to the US, the school voucher system has been used in several other countries such as Colombia, Chile, Sweden, Hong Kong, etc.
Connecting the dots:
(RSTV – DEBATE)
RSTV Discussion: The Big Picture: Project 75 India – Rajya Sabha TV (rstv.nic.in)
In News: Government has recently issued a Request for Proposal (RPF) to the two selected Indian Strategic Partners (SP) – MDL and L&T for building six conventional submarines indigenously under the Project 75 India or P-75I.
- The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has issued Request of Proposal (RFP) for the first acquisition programme under the Strategic Partnership Model for construction of six conventional submarines under Project 75 (India) for the Indian Navy.
- The two Indian selected companies are Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Larsen & Toubro (L&T), who will have to bid for the project in partnership with one each of the five foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM).
- The project is worth Rs 43,000 crore and will be the first, across services, under the strategic partnership model, which was promulgated in 2017 to boost indigenous defence manufacturing.
- The selected SPs MDL and L&T can collaborate with any of the five shortlisted OEMs, which include Naval Group of France, TKMS of Germany, JSC ROE from Russia, Daewoo Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering Co Ltd of South Korea and Navantia from Spain.
- These five foreign firms are the world leaders in the field of conventional submarine design, construction and all other related technologies.
- The foreign OEMs will be the technology partner in the SP Model and will enable SP for construction of submarines (setting up of dedicated manufacturing lines), achieving high levels of indigenization, and (Transfer of Technology) for various technologies and make India the global hub for submarine design and production.
- the RFP has key features like mandatory level of indigenous manufacture of platforms, ToT for design, manufacture, maintenance of submarines and a few critical equipment and systems, setting up of an eco-system in India for such indigenization and incentivization for other key technologies, and so on.
- The overall aim would be to progressively build indigenous capabilities in the public and private sector to design, develop and manufacture complex weapon systems for the future needs of the Armed Forces.
Project 75 India
- Project 75 India (P75I) is a project that envisaged the construction of six conventional submarines with better sensors and weapons and the Air Independent Propulsion System (AIP).
- P75I was first cleared in 2007, but lay dormant until now after undergoing numerous changes.
- The P75I project is part of a 30-year submarine building plan that ends in 2030. As part of this plan, India was to build 24 submarines — 18 conventional submarines and six nuclear-powered submarines (SSNs) — as an effective deterrent against China and Pakistan.
- Of the 14 conventional submarines India currently possesses, including the Scorpene, only half are operational at any given point of time.
- India also has two nuclear-powered submarines — INS Arihant (SSBN, a ballistic missile submarine) and INS Chakra (SSN, a nuclear-powered one) leased from Russia.
- India’s current arsenal consists of 14 conventional submarines and two nuclear-powered submarines.
- Under the strategic partnership model, an Indian shipyard will be selected by the government, which will also nominate the foreign original equipment manufacturer (OEM) under the overall arch of ‘Make in India’.
- This would provide a major boost to the indigenous design and construction capability of submarines in India, in addition to bringing in the latest submarine design and technologies as part of the project.
Significance of the project
- The project will progressively build indigenous capabilities in the public/private sector to design, develop and manufacture complex weapon systems for the future needs of the Armed Forces.
- This will be an important step towards meeting broader national objectives, encouraging self-reliance and aligning the defence sector with the “Make in India” initiative of the government.
- The project would not only aid in boosting the core submarine and ship building industry but would also greatly enhance the manufacturing and industrial sector, especially the MSME by development of an industrial eco-system for manufacture of associated spares, systems and equipment related to submarines.
CONNECTING THE DOTS:
- Discuss the significance of construction of six conventional submarines under Project 75 (India) for the Indian Navy. Also mention its objectives.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 The objective of the Dalit Bandhu scheme launched by Telangana government is associated with which of the following?
- Women Empowerment
- Health Insurance
- Entrepreneurship
- Free Education
Q.2 Which of the following is a traditional Indian herb also known as ‘Indian winter cherry’?
- Giloy
- Amla
- Turmeric
- Ashwagandha
Q.3 Which among the following is not a permanent member of the UNSC?
- China
- Russia
- France
- India
ANSWERS FOR 31st July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
Must Read
On High Inflation & Low Growth:
On Progress made by India in Poverty, Illiteracy & Food Security:
[ad_2]