[ad_1]
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Unique initiatives under Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Policies and Interventions
In news Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U), one of the world’s largest affordable housing Missions , has launched two unique initiatives.
- It has launched Khushiyon Ka Aashiyana- Short Film contest 2021 and Awas Par Samvaad which is a series of 75 seminars and workshops,to take ahead the Prime Minister’s vision of ‘Housing for All’.
- ‘Awas Par Samvaad’ aims to create awareness and promote discussion, deliberation and dissemination on ‘Housing for All’among multiple stakeholders belonging to varied streams of learning and practices, e.g. engineering, urban community development, planning, finance, etc.
- This will be done through 75 nation-wide workshops and seminars.
About Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
- Launch: 25th June 2015
- Aim: To provide housing for all in urban areas by year 2022.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Features:
- Addresses Urban housing shortage among the Urban Poor including the Slum Dwellers by ensuring a pucca house to eligible urban poor.
- It covers the entire urban area or any such authority under State legislation which is entrusted with the functions of urban planning & regulations.
- All houses under PMAY(U) have basic amenities like toilet, water supply, electricity and kitchen.
- It promotes women empowerment by providing the ownership of houses in the name of female members or in joint name.
- Preference is also given to differently abled persons, senior citizens, SCs, STs, OBCs, Minority, single women, transgender and other weaker & vulnerable sections of the society.
- It is Divided into Four Verticals:
- In-situ Rehabilitation of existing slum dwellers using land as a resource through private participation.
- Credit Linked Subsidy.
- Affordable Housing in Partnership.
- Beneficiary-led individual house construction/enhancement.
News Source: PIB
Mercury’s iron heart
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Sci & Tech
In news A study by researchers from the University of Maryland disputes the prevailing hypothesis on why Mercury has a big-sized core relative to its mantle (the layer between its core and crust).
About the new study
- Scientists had argued that hit-and-run collisions with other bodies during the formation of our solar system resulted in much of Mercury’s rocky mantle being removed, leaving behind the big, dense, metal core inside.
- But new research reveals that Sun’s magnetism is the reason for this and not the collisions.
- The researchers developed a model showing that the density, mass and iron content of a rocky planet’s core are influenced by its distance from the Sun’s magnetic field.
- There is a gradient in which the metal content in the core drops off as the four inner planets of our solar system get further from the Sun.
- The current work explains this by showing that the distribution of raw materials in the early forming solar system was controlled by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- The new model shows that during the early formation of our solar system, when the young Sun was surrounded by a swirling cloud of dust and gas, grains of iron were drawn toward the centre by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- When the planets began to form from clumps of that dust and gas, planets closer to the sun incorporated more iron into their cores than those further away.
News Source: TH
U.S., Afghanistan, Pakistan and Uzbekistan to form quad group
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news USA, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Uzbekistan have agreed in principle to establish a new quadrilateral diplomatic platform focused on enhancing regional connectivity.
- The parties intend to cooperate to expand trade, build transit links, and strengthen business-to-business ties by recognising the historic opportunity to open flourishing interregional trade routes.
Strategic location of Afghanistan
- Afghanistan’s strategic location has been touted as a competitive advantage for the country.
- Afghanistan is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north, and China to the northeast.
- It is located at the heart of the historic Silk Road.
- It was long the crossroads of commerce between Asian countries connecting them to Europe, and enhancing religious, cultural, and commercial contacts.
- The formation of the new quad group is important amid China’s desire to extend its Belt Road Initiative (BRI) to Afghanistan.
News Source: TH
G7’s Build Back Better World Initiative
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations
In news The G7 (Group of Seven) Countries proposed a ‘Build Back Better World (B3W) initiative’ at the recent 47th G7 summit to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
About B3W
- Aim: To address the infrastructure investment deficit in developing and lower income countries which is being increasingly captured by China through 2,600 BRI projects
- This infrastructure plan is being led by the United States.
- B3W initiative will provide a transparent infrastructure partnership to help narrow about $40 trillion needed by developing nations by 2035.
- It calls for spending hundreds of billions of dollars in collaboration with the private sector while adhering to climate standards and labour practices.
What is China’s BRI?
- It was launched in 2013.
- It is a multi-billion-dollar initiative that aims to link Southeast Asia, Central Asia, the Gulf region, Africa and Europe with a network of land and sea routes.
- It involves development and investment initiatives that would stretch from Asia to Europe and beyond.
- More than 100 countries have signed agreements with China to cooperate in BRI projects like railways, ports, highways and other infrastructure.
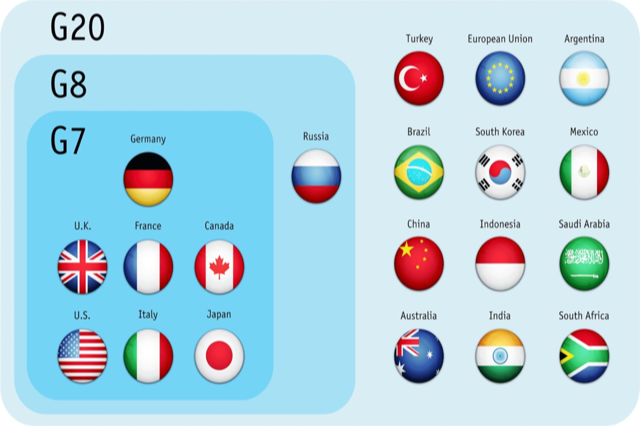
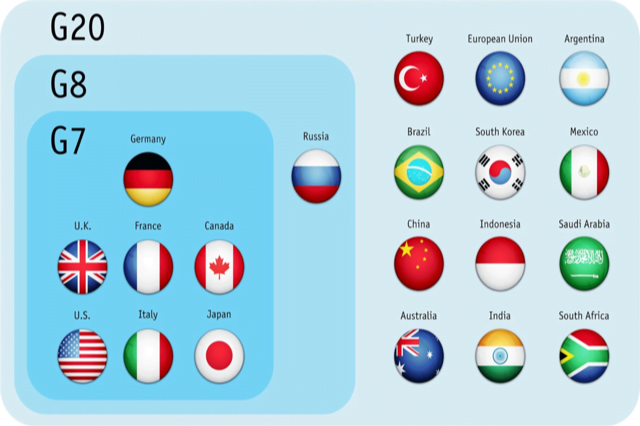
What is Group of Seven?
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975.
- The bloc meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like global economic governance, international security and energy policy.
- G7 countries: UK, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan and the US.
- All the G7 countries and India are a part of G20.
- The G7 does not have a formal constitution or a fixed headquarters.
- The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
News Source: IE
Fit for 55 Package: EU
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Conservation; Climate change
In news Recently, the European Union (EU) released a new climate proposal, the Fit for 55 package.
- The EU in December 2020 submitted a revised Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement.
What are the Aims of the proposal?
- To deliver the NDC and carbon neutrality goal through proposed changes that would ensure a fair, competitive and green transition by 2030 and beyond.
- To achieve a balance between “regulatory policies” and market-based carbon pricing to avoid the pitfalls of each.
What are the Major Proposals?
- Renewable Sources: To increase the binding target of renewable sources to 40% from 32% earlier and improve energy efficiency by 36% (from 32.5% earlier) by 2030.
- Vehicular Carbon Emissions: It must be cut by 55% by 2030 and by 100% by 2035, which means a phaseout of petrol and diesel vehicles by 2035.
- Emissions Trading System (ETS): Creation of ETS for buildings and road transport to become operational from 2026. ETS are market-based instruments that create incentives to reduce emissions where these are most cost-effective.
- Social Climate Fund: To help low-income citizens and small businesses adjust to the new ETS, the EU proposes the creation of a Social Climate Fund
- Carbon-Border Adjustment Mechanism: It will put a price on imports from places that have carbon-intensive production processes.
- Enhance Sink Capacity: It has set a target to enhance the EU’s sink capacity to 310 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent,
India’s INDC, to be achieved primarily, by 2030
- To reduce the emissions intensity of the Gross Domestic Product by about a third.
- A total of 40% of the installed capacity for electricity will be from non-fossil fuel sources.
- India also promised an additional carbon sink (a means to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere) of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by the year 2030.
- Indian Initiatives to Fight Climate Change:
News Source: DTE
AI Powered Grievance Management Application
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Policies and interventions; E-Governance
In news Recently, the Defence Minister launched an Artificial Intelligence (AI)– powered grievance management application.
- Earlier, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) launched an AI-based portal ‘SUPACE’ in the judicial system aimed at assisting judges with legal research.
About the Project
- This project is the first of its kind initiative of the Government for using AI, data science and Machine Learning techniques in grievance redressal. It is a citizen centric reform.
- Developed by: Ministry of Defence (MoD) with the help of IIT-Kanpur.
- It will automatically handle and analyse the complaints of the people and thus reduce human intervention, save time and bring more transparency in their disposal.
- Significance:
- This application will help in understanding the nature of complaints, and policy changes which can be introduced to create systemic improvements to address these grievances.
- The success of this project in MoD will pave the way for extension of this application across other Ministries.
Do you know?
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-3: RBI & Monetary Policy
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
RBI Ban on Mastercard
Context: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently banned Mastercard from issuing new debit and credit cards to customers in India with effect from July 22.
- Reason for Ban: Mastercard which is U.S. card-issuer has failed to comply with the local data storage rules announced by RBI in 2018.
What is the RBI’s data localisation policy?
- In 2018, RBI had issued a circular ordering card companies such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express to store all Indian customer data locally so that the regulator could have “unfettered supervisory access”.
- This meant that foreign card companies had to store complete information about transactions made by Indian customers in servers located within India.
- Companies were initially required to comply with these rules within six months.
- The reason offered by the RBI to back up its data localisation rule was that local storage of consumer data is necessary to protect the privacy of Indian users and also to address national security concerns.
- Since the order, Mastercard, Visa and other foreign card companies have lobbied to dilute the rules. But the RBI has remained strict that companies must comply with its data localisation rules
- Consequently, Mastercard deleted Indian customer data from its foreign servers and promised to invest in building local servers in India to store local customer data.
- The RBI, however, has not been impressed. Therefore, it has banned Mastercard from issuing new cards to customers from July 22.
What is the need for local data storage?
- Experts believe that customer privacy and national security are genuine concerns that need to be taken seriously.
- Governments may also believe that mandating foreign companies to set up local infrastructure can boost their local economies.
- Governments mandate data localisation in order to favour local companies to foreign ones.
- China, for example, has used its cyber-security laws to discriminate against foreign companies. A similar trend may be playing out in India with the Centre’s emphasis on economic self-sufficiency.
- However, many also believe that data localisation rules are too stringent and they could simply be used by governments as tools of economic protectionism.
What are the objections raised by these companies?
- Corporates also argue that formal international laws to govern the storage of digital information across borders may be sufficient to deal with these concerns.
- In 2018, Mastercard had launched a complaint with the U.S. government that PM Modi was actively promoting Indian cards like RuPay and that it was affecting the business of foreign card companies
What lies ahead?
- Business Impacted: Indian banks that are currently enrolled in the Mastercard network are expected to make alternative arrangements with other card companies. The process is expected to take a few months, and their card business is expected to take a significant hit meanwhile.
- Benefits Domestic Card Companies: The RBI’s data localisation policy, as it burdens foreign card companies, may end up favouring domestic card issuers like RuPay. The ban on American Express and Diners Club earlier this year benefited the Indian card network RuPay.
- Benefits Competitors: Mastercard owns about one-third of the market share in India, and the RBI’s ban is likely to significantly benefit its competitors.
- Impacts other foreign companies: Visa, a foreign company which dominates card payments in India, may come under regulatory pressure in the near future.
- Hurts Competition in Long Term: Thus, the card payments sector may end up being restricted to a few domestic companies, which in turn can lead to reduced competition. This could mean higher costs and lower quality services for customers.
- Continued Ambiguity on Data Ownership: Additionally, Information about spending patterns and other customer data can be monetised by companies in a variety of ways. With no clear rules on who owns customer data and to what extent, conflicts over data ownership are likely to continue for some time.
Connecting the dots :
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Which of the following Ministry launched first of its kind initiative of the Government for using AI, data science and Machine Learning techniques in grievance redressal?
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
- Ministry of Defence
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
- It aims to provide housing for all in urban areas by year 2022.
- It is implemented by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Which of the following has launched Fit for 55 Package?
- USA
- European Union
- China
- Russia
ANSWERS FOR 17th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
Must Read
On GST:
On China’s QUAD:
On Social Security for Informal Workers:
[ad_2]