[ad_1]
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
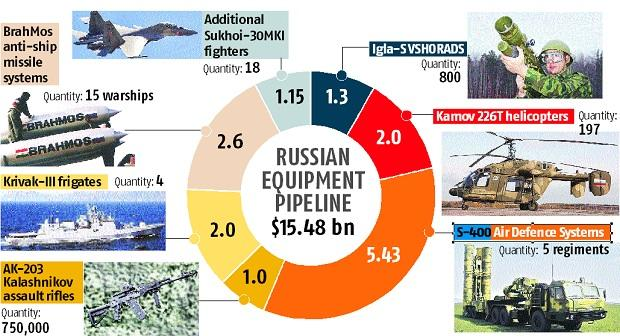
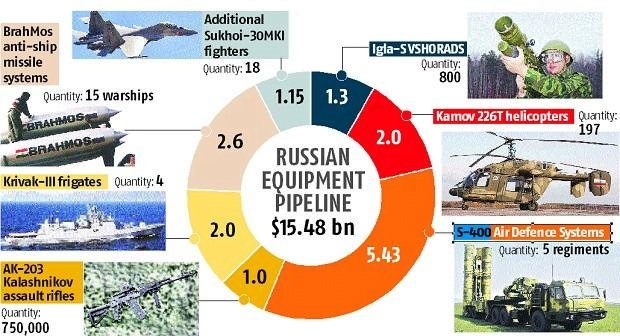
Krivak Stealth Frigates
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Defence and Security
In news
- Recently, the Vice-Chief of the Naval Staff has inaugurated the construction of the second frigate of the Krivak or Talwar class.
- The construction of the first ship was laid in January, 2021. It would be delivered in 2026 and the second ship after six months.
About the Krivak
- The Krivak class stealth ships are being built with technology transfer from Russia by Goa Shipyard Ltd. (GSL) under ‘Make in India’.
- Engines for the ships are supplied by Ukraine.
- In October 2016, India and Russia signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) for four Krivak or Talwar stealth frigates.
- The first two frigates will be built in Yantar Shipyard, in Kaliningrad, Russia. The following two will be built in GSL.
- The new Krivak frigates will have the same engines and armament configuration as Yantar’s last three frigates – INS Teg, Tarkash and Trikand.
- These will be armed with BrahMos anti-ship and land attack missiles.
- Use:
- Accomplish a wide variety of naval missions such as finding and eliminating enemy submarines and large surface ships.
Pic courtesy: BS
Proposal to Ban ‘Flash sales’ on E-commerce Sites
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – E-commerce
In news
- The government proposed changes to the Consumer Protection (e-commerce) Rules 2020, banning all “flash sales” in order to monitor the deep discounts offered on e-commerce websites.
Rationale for Making Changes
- Conventional flash sales by third party sellers are not banned on e-commerce platforms but only the predatory ones.
- Small businesses complain of misuse of market dominance and deep discounting by e-commerce marketplaces such as Amazon and Flipkart.
- Certain e-commerce entities are engaging in limiting consumer choice by indulging in ‘back to back’ or ‘flash’ sales wherein one seller on a platform does not carry any inventory or order fulfilment capability but merely places a ‘flash or back to back’ order with another seller controlled by platform.
Other Important Proposals
- The e-commerce sites are also directed to ensure appointment of Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) for 24×7 coordination with law enforcement agencies.
- These companies will also have to name a resident grievance officer who has to be a company employee and a citizen of India.
- To tackle growing concerns of preferential treatment, the new rules propose to ensure none of the related parties are allowed to use any consumer information for ‘unfair advantage’.
- The companies will also have to identify goods based on their country of origin and provide a filter mechanism at a pre-purchase stage for customers.
- They will also have to offer alternatives to these imported goods to provide a “fair opportunity” to domestic sellers.
- In the event a seller fails to deliver a good or service, the final liability will fall on the e-commerce marketplace.
- E-commerce firms operating in India will also have to register under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
About E-Commerce
- Electronic commerce (e-commerce) is a business model that lets firms and individuals buy and sell things over the Internet.
- The Indian e-commerce market is expected to grow to USD 200 billion by 2026 from USD 38.5 billion in 2017 due to following reasons:.
- Rising smartphone penetration
- The launch of 4G networks
- Increasing consumer wealth
- It is expected to surpass the US to become the second-largest e-commerce market in the world by 2034.
Electronic Weighing Machines at Fair Price Shops
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- The Central Government has asked the States Governments to buy electronic weighing machines for ration shops from electronic Point of Sale devices (ePoS) savings.
- For this, the Ministry of Consumer Affairs has amended the Food Security (Assistance To State Government Rules) 2015 to encourage the states to generate savings through judicious use of e-PoS devices.
- Benefits:
- The integration of ePoS devices with electronic weighing scales will ensure the right quantity to beneficiaries being covered under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- It will ensure greater transparency in the Public distribution system (PDS) regime.
- It will reduce food grain leakages.
- Subsidised food grains provided to the rightful beneficiary through biometric authentication.
About National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- Objective: To provide for food and nutritional security in the human life cycle approach, by ensuring access to adequate quantities of quality food at affordable prices to people to live a life with dignity.
- Coverage: 75% of the rural population and upto 50% of the urban population for receiving subsidized foodgrains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Eligibility:
- Priority Households to be covered under TPDS, according to guidelines by the State government.
- Households covered under existing Antyodaya Anna Yojana.
- Provisions:
- 5 Kgs of foodgrains per person per month at Rs. 3/2/1 per Kg for rice/wheat/coarse grains.
- The existing AAY household will continue to receive 35 Kgs of foodgrains per household per month.
- Meal and maternity benefit of not less than Rs. 6,000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers during pregnancy and six months after the child birth.
- Meals to children upto 14 years of age.
- Food security allowance to beneficiaries in case of non-supply of entitled foodgrains or meals.
- Setting up of grievance redressal mechanisms at the district and state level.
Delimitation in Jammu and Kashmir started
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Polity and Governance
In news
- Recently, the delimitation exercise has started in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K).
- The completion of the delimitation exercise will mark the political process in the Union Territory (UT) that has been under Centre’s rule since June 2018.
- After the abrogation of its special status under Article 370, on 5th August, 2019, a special delimitation commission was constituted in March, 2020 to carve out Assembly and Parliament seats in the UT.
What is Delimitation?
- It is the act of fixing or redrawing the boundaries of territorial constituencies in a country or a province having a legislative body, as per the Election Commission.
- The delimitation exercise is carried out by an independent high-powered panel known as the Delimitation Commission whose orders have the force of law and cannot be questioned by any court.
- Aim:
- To have equal representation to equal segments of the population in order to ensure a fair division of geographical areas.
Constitutional Basis for Delimitation
- Article 82: The Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act after every Census.
- Article 170: States also get divided into territorial constituencies as per Delimitation Act after every Census.
Delimitation Commission:
- The Delimitation Commission is appointed by the President of India.
- It works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
- Composition:
- Retired Supreme Court judge
- Chief Election Commissioner
- Respective State Election Commissioners.
National Population Register (NPR)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – Citizenship
In news
- According to a Union Home Ministry manual, migrants belonging to six non-Muslim minority communities from Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh, while applying for long-term visas (LTVs), can also produce National Population Register (NPR) enrolment slips as proof of the duration of their stay in India.
- The NPR number is part of an illustrative list of more than 10 documents that could be provided to apply for an LTV, which is a precursor to acquiring Indian citizenship either by naturalisation or registration under Section 5 and 6 of the Citizenship Act, 1955, for the six Non-Muslim communities
- These communities are: Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, Parsis, Christians and Buddhists
- The special provision of LTVs for Hindus and Sikhs from Pakistan and Afghanistan was first made in 2011.
- It was also asserted that the awareness drive is not related to the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA), which is intended to benefit undocumented migrants from the six groups who entered India before the 2014 cut-off date.
- The CAA is yet to be implemented.
About NPR
- The NPR was first compiled in 2010 simultaneously with the decadal Census exercise and later updated in 2015.
- It already has a database of 119 crore residents.
- The NPR is a register of usual residents linked with location particulars down to the village level.
- It is updated periodically “to incorporate the changes due to birth, death and migration”.
- The next phase of the NPR, expected to include contentious questions on date and place of birth of father and mother, last place of residence and mother tongue, was to be simultaneously updated with the 2021 House Listing and Housing Census that has been indefinitely postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Miscellaneous
Land for Life Award: UN
-
Recently, Shyam Sundar Jyani, a Rajasthan-based climate activist, has won the prestigious United Nations’ Land for Life Award for his environment conservation concept, Familial Forestry.
- Familial Forestry means transferring the care of the tree and environment in the family so that a tree becomes a part of the family’s consciousness.
- Every two years, the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) organizes the Land for Life Award.
- The Award recognizes excellence and innovation in efforts towards land in balance.
- The Award was launched in 2011 at the UNCCD Conference of Parties (COP)10 in the Republic of Korea as part of the Changwon Initiative.
-
- The Changwon Initiative intends to complement activities being undertaken in line with The Strategy (for 2008-18) and in accordance with COP 10 decisions.
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
National Population Register (NPR)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – Citizenship
In news
- According to a Union Home Ministry manual, migrants belonging to six non-Muslim minority communities from Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh, while applying for long-term visas (LTVs), can also produce National Population Register (NPR) enrolment slips as proof of the duration of their stay in India.
- The NPR number is part of an illustrative list of more than 10 documents that could be provided to apply for an LTV, which is a precursor to acquiring Indian citizenship either by naturalisation or registration under Section 5 and 6 of the Citizenship Act, 1955, for the six Non-Muslim communities
- These communities are: Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, Parsis, Christians and Buddhists
- The special provision of LTVs for Hindus and Sikhs from Pakistan and Afghanistan was first made in 2011.
- It was also asserted that the awareness drive is not related to the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA), which is intended to benefit undocumented migrants from the six groups who entered India before the 2014 cut-off date.
- The CAA is yet to be implemented.
About NPR
- The NPR was first compiled in 2010 simultaneously with the decadal Census exercise and later updated in 2015.
- It already has a database of 119 crore residents.
- The NPR is a register of usual residents linked with location particulars down to the village level.
- It is updated periodically “to incorporate the changes due to birth, death and migration”.
- The next phase of the NPR, expected to include contentious questions on date and place of birth of father and mother, last place of residence and mother tongue, was to be simultaneously updated with the 2021 House Listing and Housing Census that has been indefinitely postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Context: The government has proposed changes to the e-commerce rules under the Consumer Protection Act to make the framework under which firms operate more stringent.
Key Changes mooted are:
- Commonalities with the IT intermediary rules: The draft rules also stipulate the appointment of a chief compliance officer, a nodal contact person for 24×7 coordination with law enforcement agencies.
- Fall-back liability: Here, e-commerce firms will be held liable in case a seller on their platform fails to deliver goods or services due to negligent conduct, which causes loss to the customer. Earlier, the platform used to direct an aggrieved person to seller, now they will be able to reach out to the platform itself.
- Fair platform: The rules propose to restrict e-commerce companies from “manipulating search results or search indexes” so as to prevent preferential treatment to certain products.
- Push for made-in-India products: E-commerce entities offering imported goods or services to ‘incorporate a filter mechanism to identify goods based on country of origin and suggest alternatives to ensure a fair opportunity to domestic goods’.
- Ban of “specific flash sales” by e-commerce entities: While as per the draft rules, conventional e-commerce flash sales are not banned, specific flash sales or back-to-back sales “which limit customer choice, increase prices and prevents a level playing field are not allowed”.
- Integration with Consumer Helpline: The draft amendment also proposes to ask e-commerce firms to mandatorily become a part of the National Consumer Helpline
Other proposals
- Registration has also been made mandatory for all e-commerce players
- Any entity having 10 per cent or more common ultimate beneficial ownership will be considered an “associated enterprise” of an e-commerce platform.
- All entities must provide information within 72 hours on any request made by an authorised government agency probing any breach of law including cybersecurity issues.
Analysis of the draft rules
- Greater Oversight by Government: Following the enactment of New IT Rules, the draft e-commerce amendments show the Government’s increasing keenness to exercise greater oversight over all online platforms.
- Fair Market practices: There were accusations that the pricing practices of two large e-commerce giants (Amazon and Walmart owned Flipkart) are skewed to favour select sellers on their platforms. The draft rules aim to makes marketplaces fair & level playing to all.
- Level playing field for offline retailers: The deep-pocketed e-commerce companies have adopted deep discounting strategies to enhance their market share. This predatory business practices have hurt offline retailers. New rules aim to rectify this.
Concerns
- The enforcement of many of these norms is bound to spur protracted legal fights.
- The Government appears to be going back to an era of tight controls.
- Overregulation with scope for interpretative ambiguity risks retarding growth and job creation in the hitherto expanding e-commerce sector.
Connecting the dots:
JUDICIARY/ ETHICS
Topic:
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Judiciary
Recusal of Judges
Context: Recently, two Supreme Court judges — Justice Indira Banerjee and Justice Aniruddha Bose — have recused themselves from hearing cases relating to West Bengal.
Recusal = Withdrawal of a judge or prosecutor from a case on the grounds that they are unqualified to perform legal duties because of a possible conflict of interest or lack of impartiality
Why does a judge recuse?
- To Prevent Perception of Bias: When there is a conflict of interest, a judge can withdraw from hearing a case to prevent creating a perception that he carried a bias while deciding the case.
- Nemo judex in causa sua: This latin term translates to “nobody should be a judge in his/her own case” which is a cardinal principle of due process of law.
- Fair & Trustworthy system: Any interest or conflict of interest should be a ground to withdraw from a case since a judge has a duty to act fair. Recusal during such situation leads to reliable, trustworthy judicial system.
In what all situations conflict of interest usually arises?
The conflict of interest can be in many ways —
- If a judge is holding shares in a company that is a litigant in the case being heard
- If a judge is having/had a prior or personal association with a party involved in the case.
- When an appeal is filed in the Supreme Court against a judgement of a High Court that may have been delivered by the SC judge when she was in the HC.
What is the process for recusal?
- The decision to recuse generally comes from the judge herself as it rests on the conscience and discretion of the judge to disclose any potential conflict of interest.
- In some circumstances, lawyers or parties in the case bring it up before the judge.
- If a judge recuses, the case is listed before the Chief Justice for allotment to a fresh Bench.
- There are no formal rules governing recusals, although several Supreme Court judgments have dealt with the issue (Ex: Ranjit Thakur v Union of India, 1987)
Can a judge refuse to recuse?
- Once a request is made for recusal, the decision to recuse or not rests with the judge.
- While there are some instances where judges have recused even if they do not see a conflict but only because such an apprehension was cast, there have also been several cases where judges have refused to withdraw from a case.
- In the Ayodhya-Ramjanmabhoomi case, Justice U U Lalit recused himself from the Constitution Bench after parties brought to his attention that he had appeared as a lawyer in a criminal case relating to the case.
- In 2019, Justice Arun Mishra had controversially refused to recuse himself from a Constitution Bench set up to re-examine a judgement he had delivered previously on 2013 Land Acquisition law.
Do judges record reasons for recusal?
- Since there are no formal rules governing the process, it is often left to individual judges to record reasons for recusal.
- Some judges disclose the reasons in open court; in some cases, the reasons are apparent.
- In a landmark verdict in 2015 holding that the National Judicial Appointments Commission as unconstitutional, Justice Kurian Joseph and Justice Madan Lokur had referred to the need for judges to give reasons for recusal to build transparency and help frame rules to govern the process.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASPuucho are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 United Nations’ Land for Life Award is organised by which of the following?
- UNICEF
- WHO
- UNFCCC
- UNCCD
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- 75% of the rural population and upto 50% of the urban population are covered under it.
- Meal and maternity benefit of not less than Rs. 6,000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers during pregnancy and twelve months after the child birth.
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Delimitation Commission:
- It is appointed by the President of India.
- It works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 22nd June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
Must Read
On soft power comparison between India and China:
On Fertilizer subsidy:
On ongoing farmers protest:
[ad_2]