[ad_1]
INSIGHTS STATIC QUIZ 2020 – 21
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
-
Question 1 of 5
Consider the following statements.
- The First Lok Sabha met on the eve of the first republic day.
- India ceased to be a British dominion immediately post-enactment of the constitution.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
CorrectSolution: b)
The First Lok Sabha was constituted on 17 April 1952 after India’s first general election.
The Indian Independence Act 1947 merely converted India into a British dominion. It ceased to be dominion only after 26th January 1950.
Till 1952, the Constituent assembly itself functioned as the law-making body.
It was only after the first general elections that Lok Sabha was constituted and the assembly was relived of its responsibility of acting as a dual body.
IncorrectSolution: b)
The First Lok Sabha was constituted on 17 April 1952 after India’s first general election.
The Indian Independence Act 1947 merely converted India into a British dominion. It ceased to be dominion only after 26th January 1950.
Till 1952, the Constituent assembly itself functioned as the law-making body.
It was only after the first general elections that Lok Sabha was constituted and the assembly was relived of its responsibility of acting as a dual body.
-
Question 2 of 5
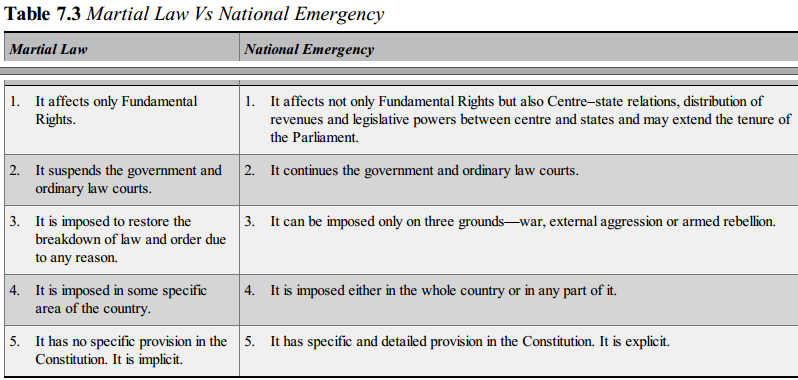
Consider the following statements regarding Martial Law
- It affects only Fundamental Rights
- It is imposed in the whole country.
- It has no specific provision in the Constitution
- It is imposed to restore the breakdown of law and order due to any reason.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
CorrectSolution: a)
 Incorrect
IncorrectSolution: a)

-
Question 3 of 5
If a bill seeks to amend the federal provisions of the Constitution
CorrectSolution: d)
If the bill seeks to amend the federal provisions of the Constitution, it must also be ratified by the legislatures of half of the states by a simple majority. (No special majority or two-thirds states are needed.)
After duly passed by both the Houses of Parliament and ratified by the state legislatures, where necessary, the bill is presented to the President for assent. (No prior consent is required.)
IncorrectSolution: d)
If the bill seeks to amend the federal provisions of the Constitution, it must also be ratified by the legislatures of half of the states by a simple majority. (No special majority or two-thirds states are needed.)
After duly passed by both the Houses of Parliament and ratified by the state legislatures, where necessary, the bill is presented to the President for assent. (No prior consent is required.)
-
Question 4 of 5
Consider the following statements regarding the features of Cabinet Committees in India?
- They are mentioned in the Constitution and the Rules of Business of Council of Ministers.
- They cannot take final decisions on matters referred to them by the Cabinet.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
CorrectSolution: a)
They are extra-constitutional in emergence. In other words, they are not mentioned in the Constitution. However, the Rules of Business provide for their establishment.
They not only sort out issues and formulate proposals for the consideration of the Cabinet, but also take decisions. However, the Cabinet can review their decisions.
They are an organisational device to reduce the enormous workload of the Cabinet. They also facilitate in-depth examination of policy issues and effective coordination.
IncorrectSolution: a)
They are extra-constitutional in emergence. In other words, they are not mentioned in the Constitution. However, the Rules of Business provide for their establishment.
They not only sort out issues and formulate proposals for the consideration of the Cabinet, but also take decisions. However, the Cabinet can review their decisions.
They are an organisational device to reduce the enormous workload of the Cabinet. They also facilitate in-depth examination of policy issues and effective coordination.
-
Question 5 of 5
The Parliament can abolish a legislative council only
CorrectSolution: b)
The Constitution provides for the abolition or creation of legislative councils in states.
Accordingly, the Parliament can abolish a legislative council (where it already exists) or create it (where it does not exist), if the legislative assembly of the concerned state passes a resolution to that effect.
Such a specific resolution must be passed by the state assembly by a special majority, that is, a majority of the total membership of the assembly and a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of the assembly present and voting.
IncorrectSolution: b)
The Constitution provides for the abolition or creation of legislative councils in states.
Accordingly, the Parliament can abolish a legislative council (where it already exists) or create it (where it does not exist), if the legislative assembly of the concerned state passes a resolution to that effect.
Such a specific resolution must be passed by the state assembly by a special majority, that is, a majority of the total membership of the assembly and a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of the assembly present and voting.
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE for Motivation and Fast Updates
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Motivational and New analysis videos
[ad_2]